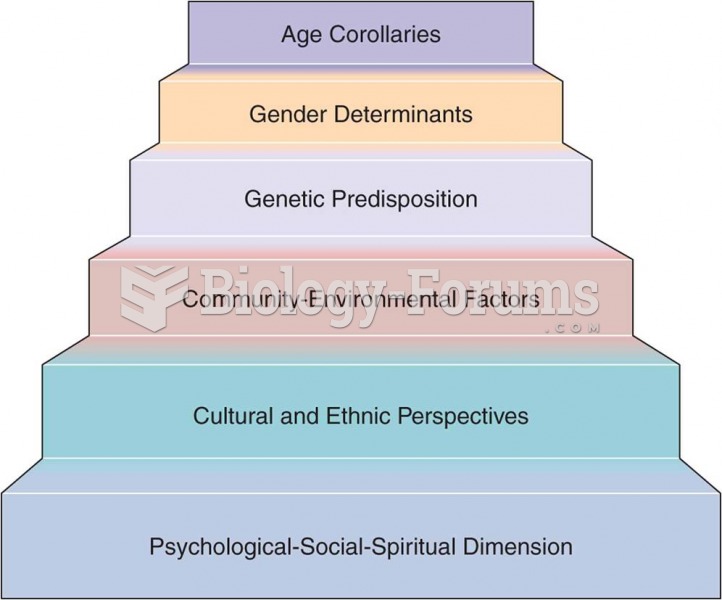
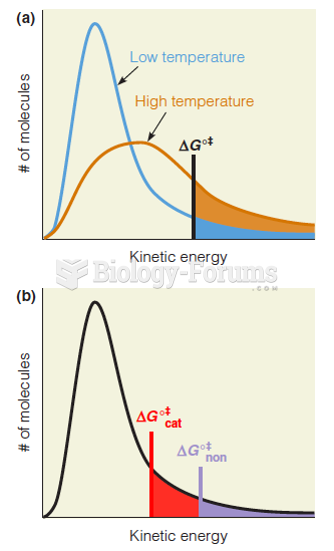
|
|
|
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.