This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Did you know?
Complications of influenza include: bacterial pneumonia, ear and sinus infections, dehydration, and worsening of chronic conditions such as asthma, congestive heart failure, or diabetes.
Did you know?
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
Did you know?
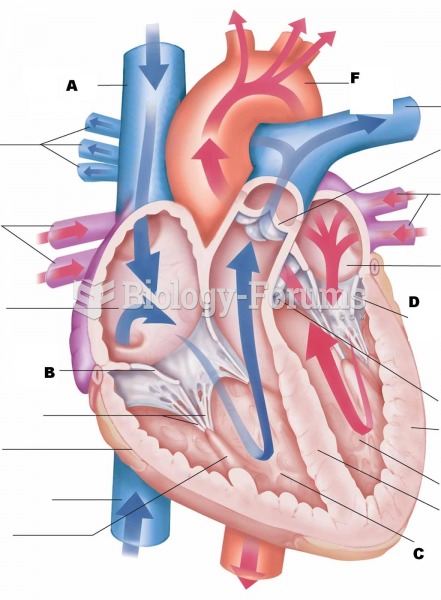
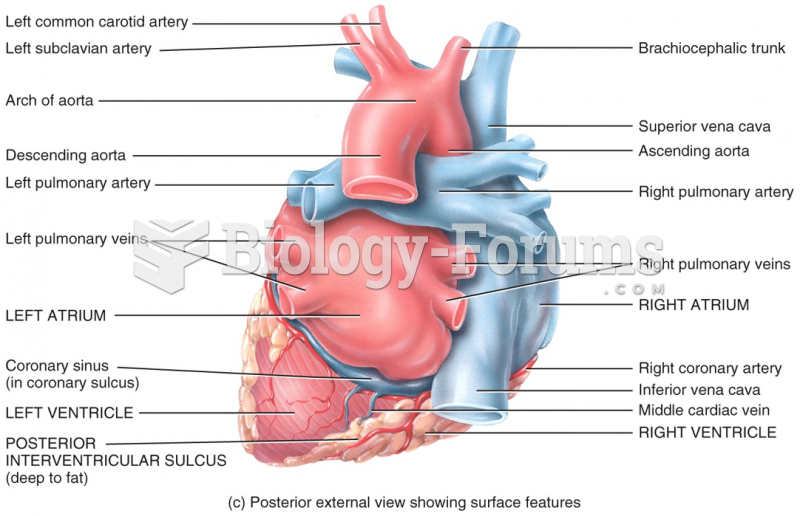
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Did you know?
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.