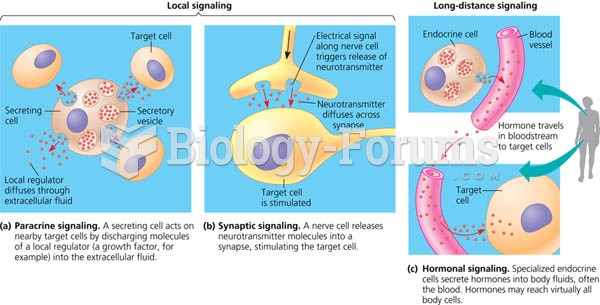
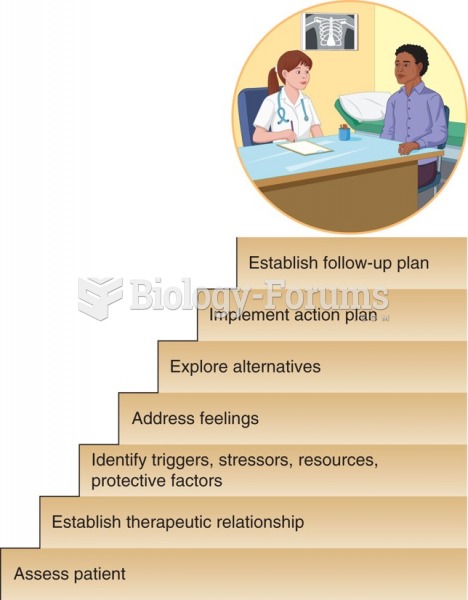
|
|
|
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
Today, nearly 8 out of 10 pregnant women living with HIV (about 1.1 million), receive antiretrovirals.