|
|
|
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
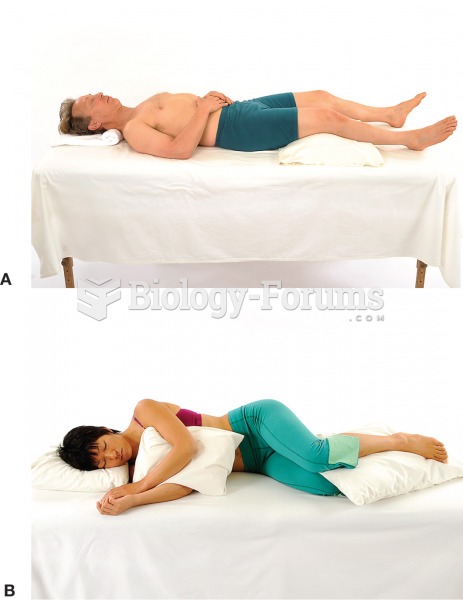 a) Using a soft pillow rather than a hard bolster under the knees will reduce pressure on the back ...
a) Using a soft pillow rather than a hard bolster under the knees will reduce pressure on the back ...
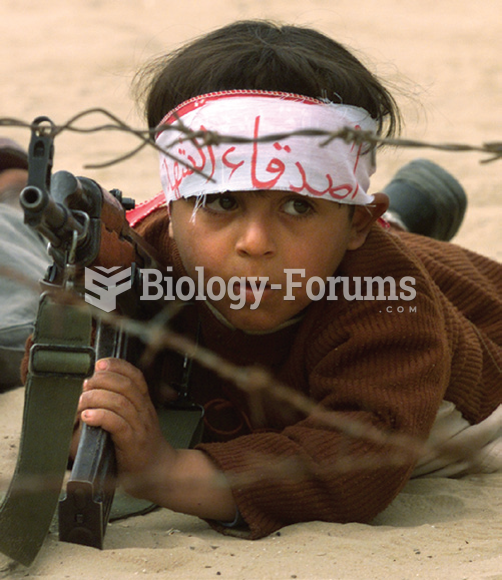 The hatred and vengeance of adults become the children’s heritage. The headband of this 4-year-old ...
The hatred and vengeance of adults become the children’s heritage. The headband of this 4-year-old ...
 Apply two-hand petrissage over the entire upper back. Place palms flat on back next to each other. ...
Apply two-hand petrissage over the entire upper back. Place palms flat on back next to each other. ...