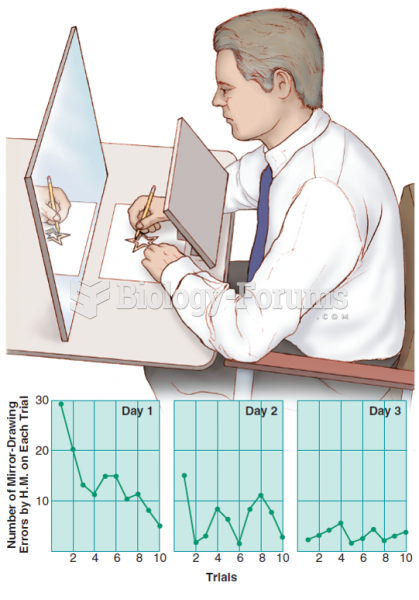
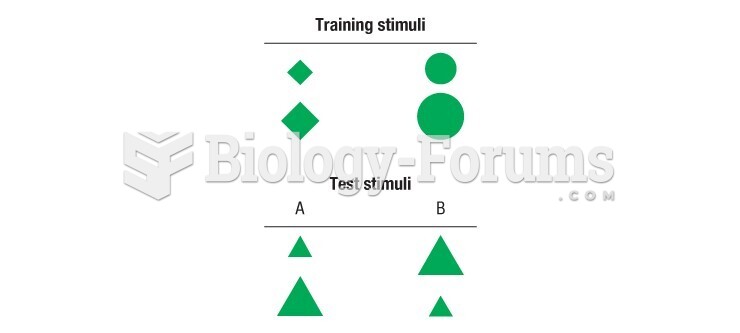
|
|
|
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
 Sociologists study the social factors that underlie human behavior, the experiences that mold us, ...
Sociologists study the social factors that underlie human behavior, the experiences that mold us, ...
 From your experiences in grade school, can you tell if or how your teachers unintentionally helped ...
From your experiences in grade school, can you tell if or how your teachers unintentionally helped ...