|
|
|
Many supplement containers do not even contain what their labels say. There are many documented reports of products containing much less, or more, that what is listed on their labels. They may also contain undisclosed prescription drugs and even contaminants.
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
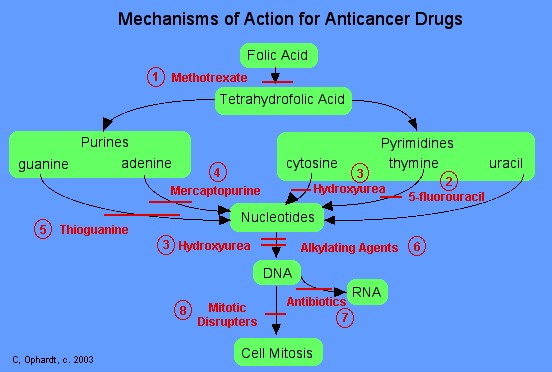
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.