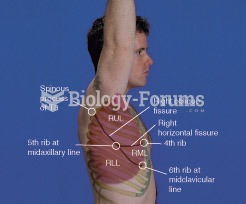
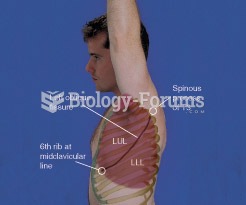
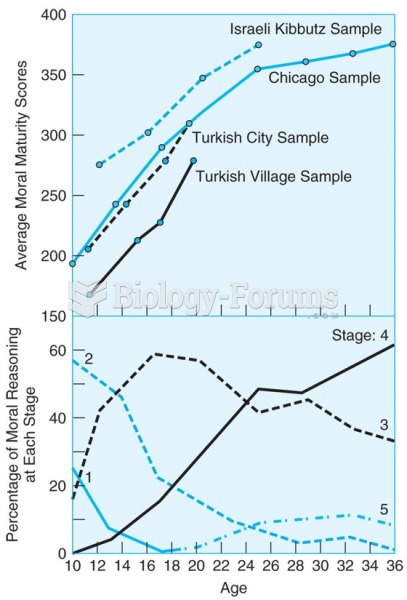
|
|
|
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.