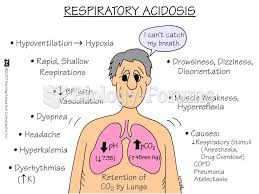
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
HIV testing reach is still limited. An estimated 40% of people with HIV (more than 14 million) remain undiagnosed and do not know their infection status.
Did you know?
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
Did you know?
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Did you know?
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
Did you know?
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.


![GEN. BIO. TEST HELP [EMERGENCY]](https://biology-forums.com/gallery/47/medium_126671_18_12_13_12_37_01.png)