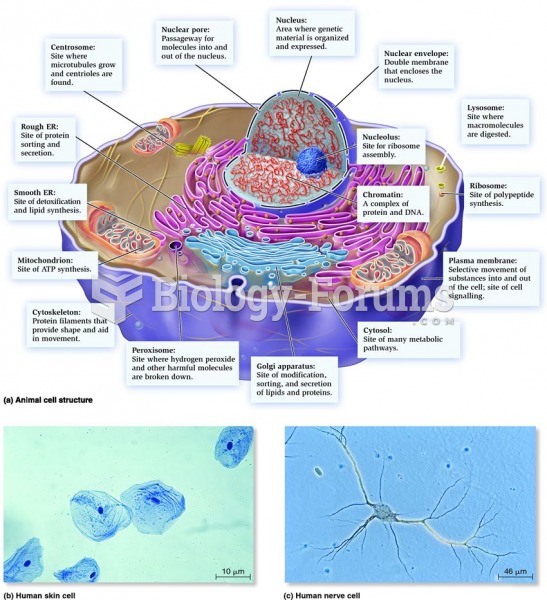
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Did you know?
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
Did you know?
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.