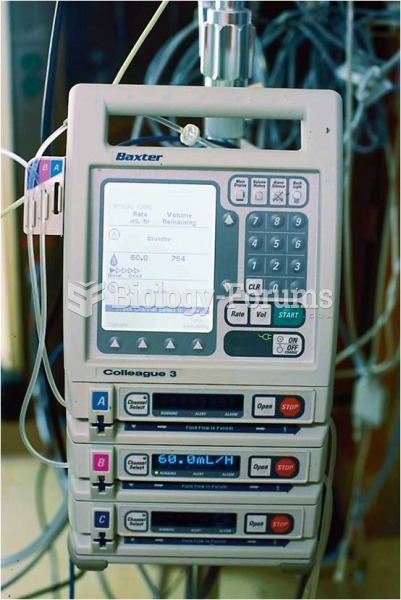
|
|
|
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.