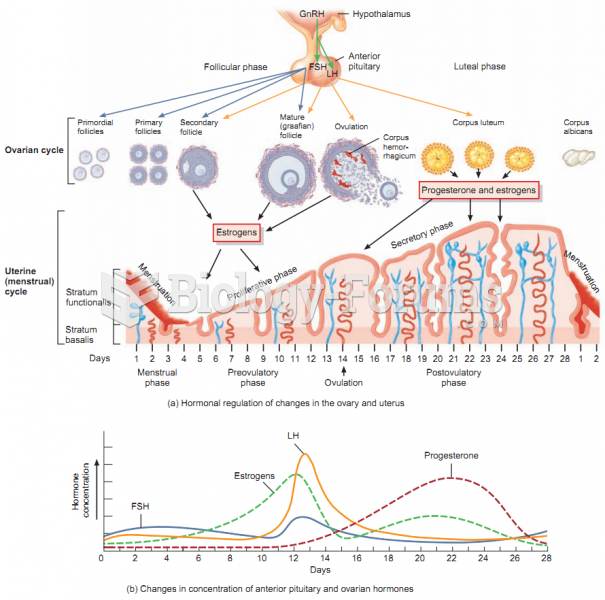
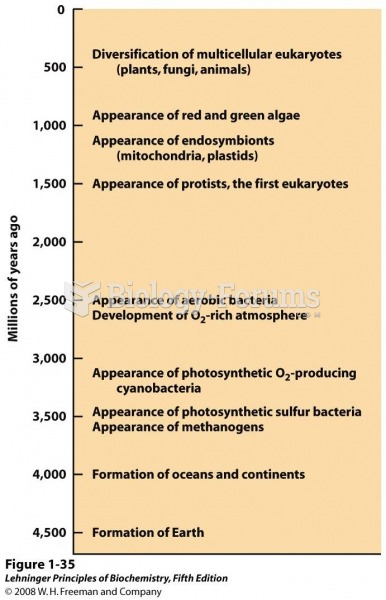
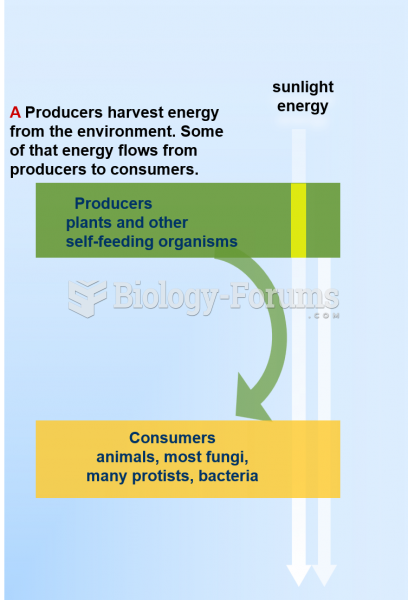
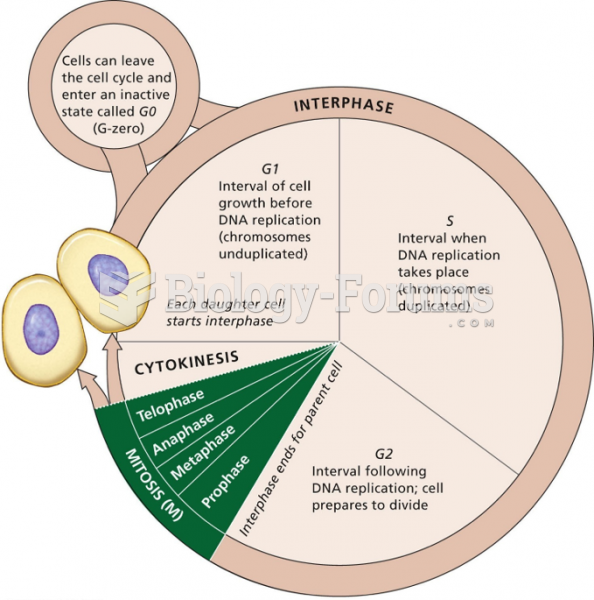
|
|
|
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.
Nearly all drugs pass into human breast milk. How often a drug is taken influences the amount of drug that will pass into the milk. Medications taken 30 to 60 minutes before breastfeeding are likely to be at peak blood levels when the baby is nursing.
Although not all of the following muscle groups are commonly used, intramuscular injections may be given into the abdominals, biceps, calves, deltoids, gluteals, laterals, pectorals, quadriceps, trapezoids, and triceps.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.