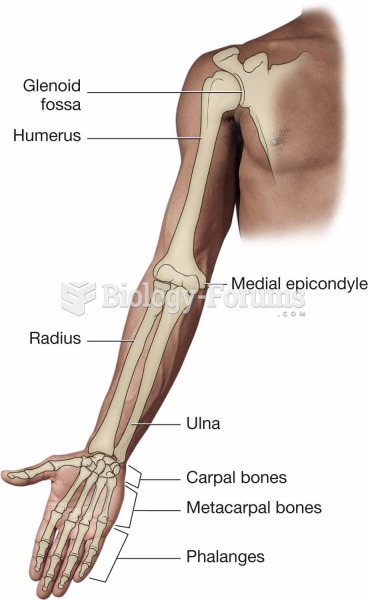
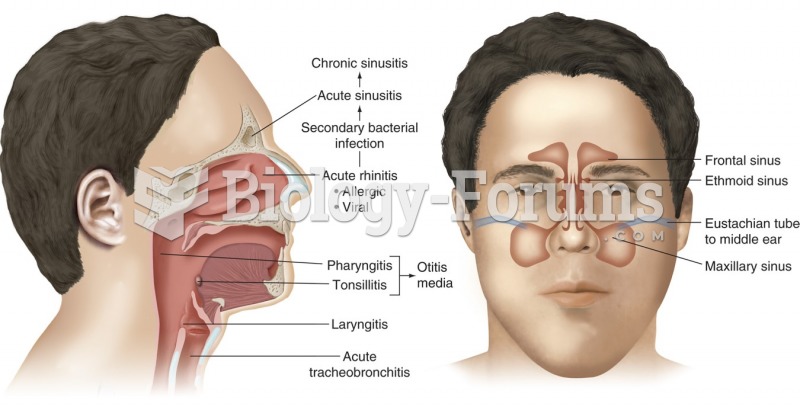
|
|
|
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Immunoglobulin injections may give short-term protection against, or reduce severity of certain diseases. They help people who have an inherited problem making their own antibodies, or those who are having certain types of cancer treatments.