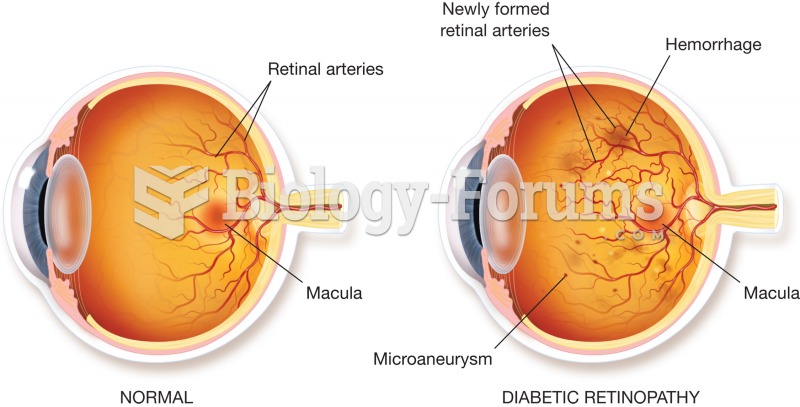
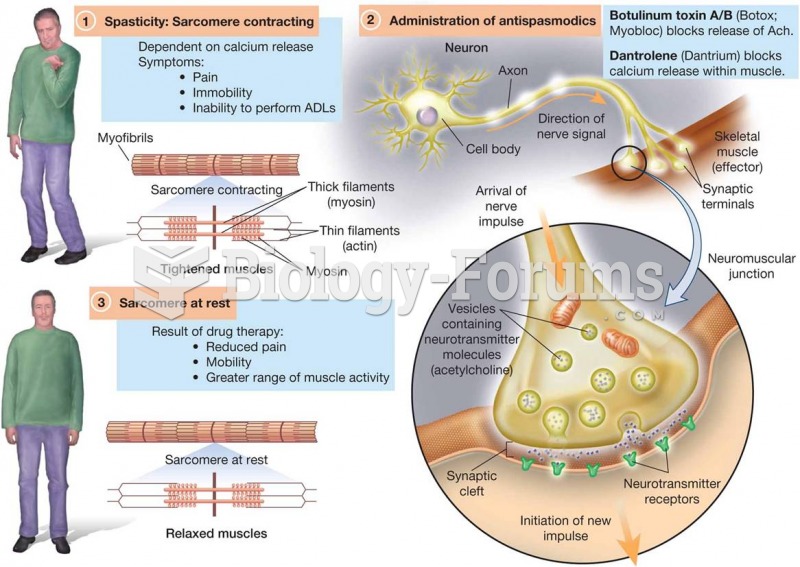
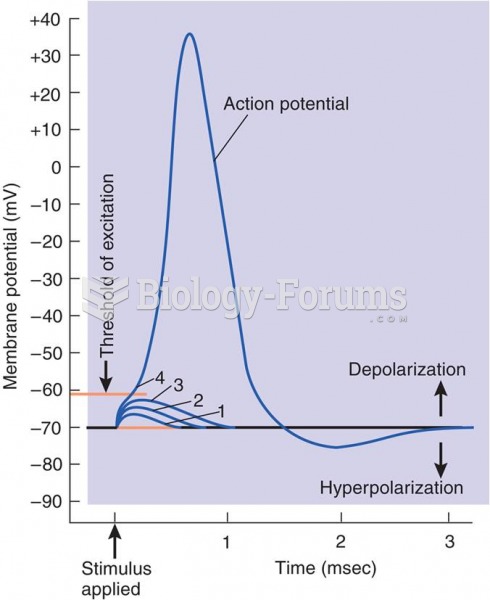
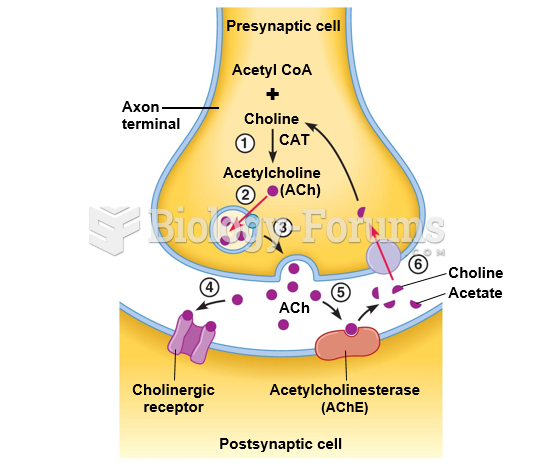
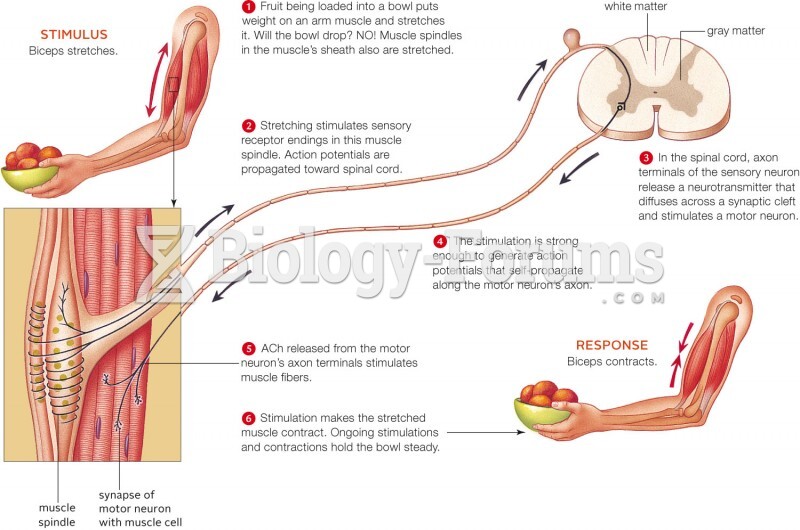
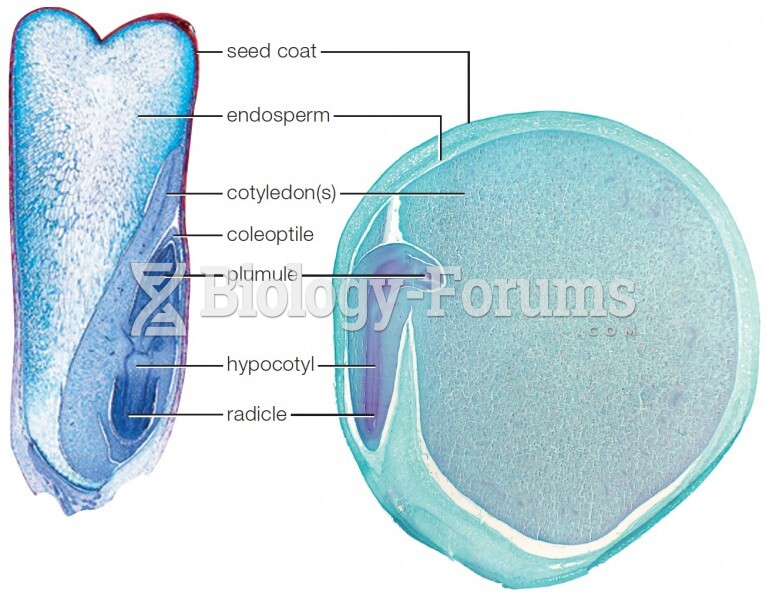
|
|
|
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.