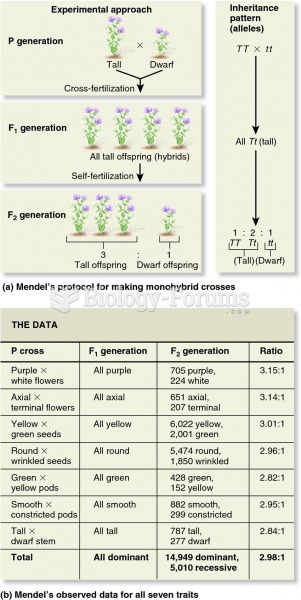
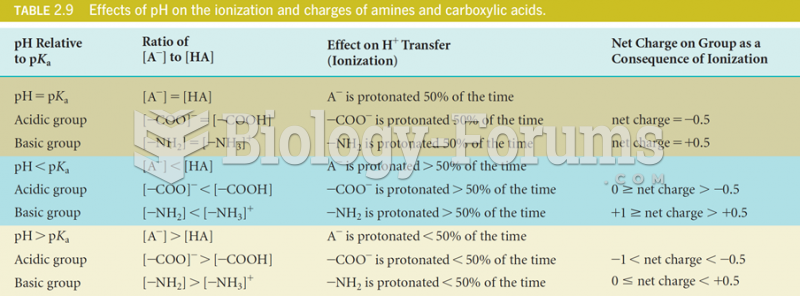
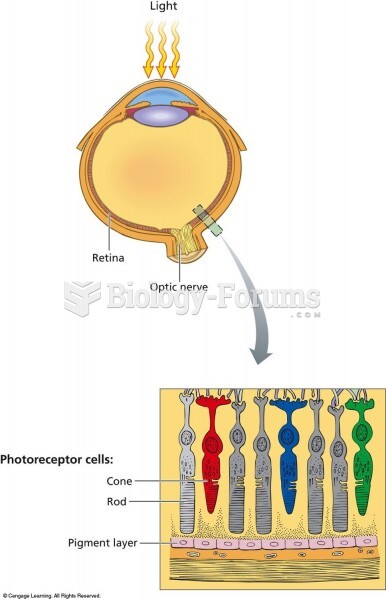
|
|
|
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.