|
|
|
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
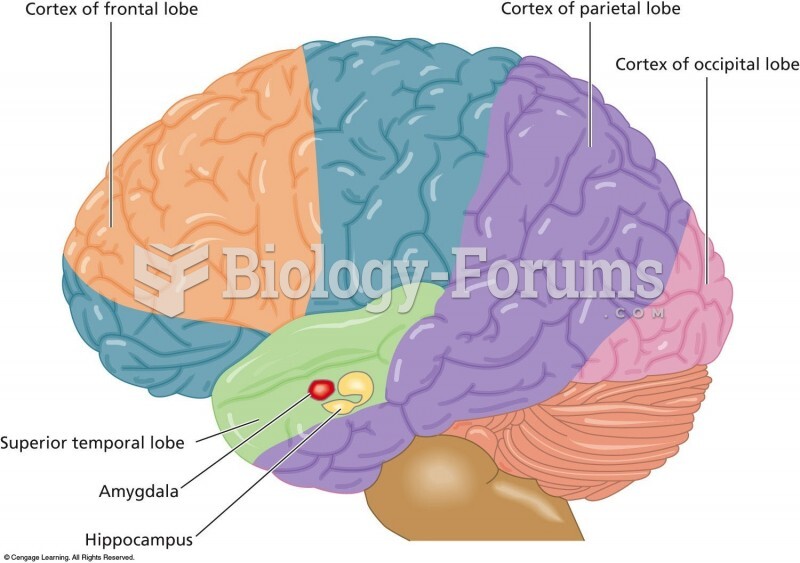
Egg cells are about the size of a grain of sand. They are formed inside of a female's ovaries before she is even born.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.