|
|
|
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
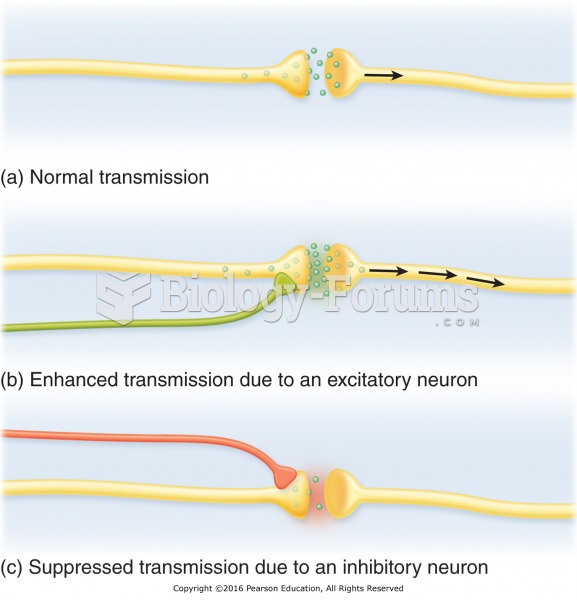
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.
Historic treatments for rheumatoid arthritis have included gold salts, acupuncture, a diet consisting of apples or rhubarb, nutmeg, nettles, bee venom, bracelets made of copper, prayer, rest, tooth extractions, fasting, honey, vitamins, insulin, snow collected on Christmas, magnets, and electric convulsion therapy.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.