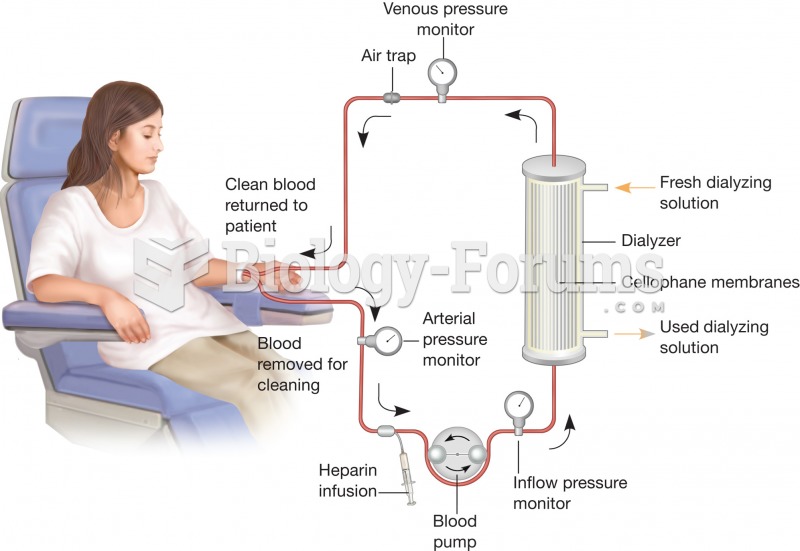
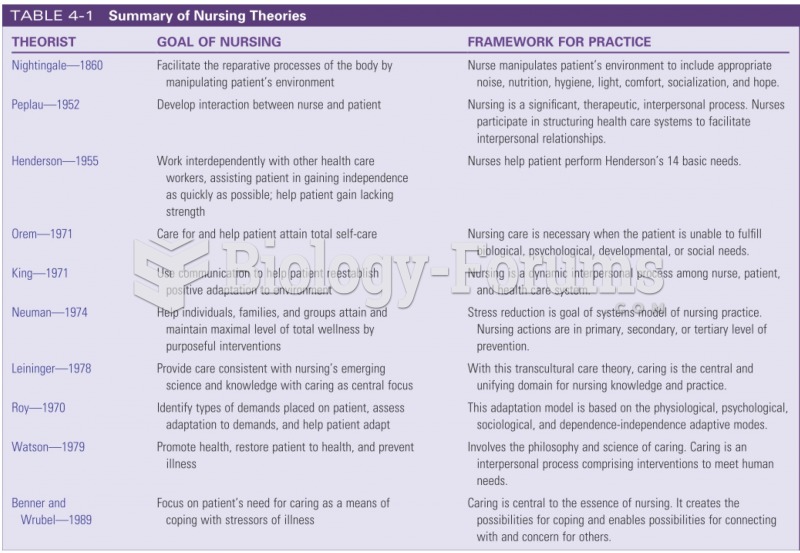
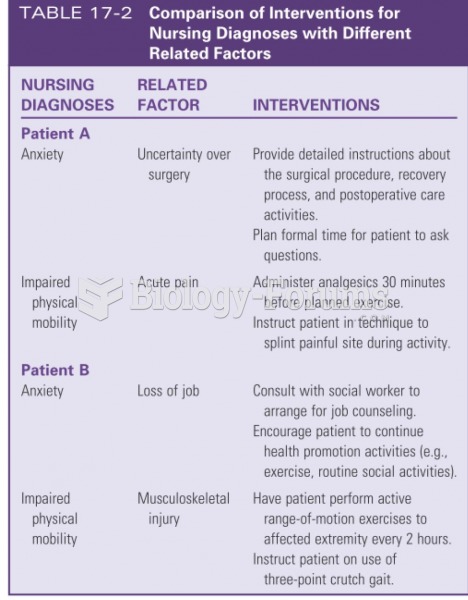
Answer to Question 1
ANS: B
The nursing process is cyclic rather than linear. As an individual patient's condition changes, so does the way a professional nurse thinks about that patient's needs, forcing modification of earlier plans of care. The dynamic, responsive nature of the nursing process allows it to be used effectively with patients in any setting and at every level of care. The plan of care is individualized for the patient on the basis of assessment findings, changing needs, setting, and timing of interaction, not just outcomes. Following the steps of the nursing process ensures that patient care is well organized and thorough. Collaboration among several members of the health care team is often required to adequately address patient needs. In many cases, nurses incorporate orders from a primary care provider, nursing interventions, and input from others, such as physical therapists, social workers, or respiratory therapists, into a patient's plan of care to help alleviate patient problems and achieve established patient-centered goals and outcomes.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: C
The nursing process is adaptable for developing plans of care for individuals who are hospitalized or are receiving care in an outpatient, long-term care, or home setting. It is an equally useful method for addressing the needs of a specific population. Decisions regarding which nursing interventions and medical treatments to implement are made on the basis of safety and their effectiveness in meeting a patient's identified needs and desired outcomes. The dynamic, responsive nature of the nursing process allows it to be used effectively with patients in any setting and at every level of care. The plan of care is individualized for the patient on the basis of assessment findings, changing needs, setting, and timing of interaction, not just outcomes. Following the steps of the nursing process ensures that patient care is well organized and thorough. Collaboration among several members of the health care team is often required to adequately address patient needs. In many cases, nurses incorporate orders from a primary care provider, nursing interventions, and input from others, such as physical therapists, social workers, or respiratory therapists, into a patient's plan of care to help alleviate patient problems and achieve established patient-centered goals and outcomes.