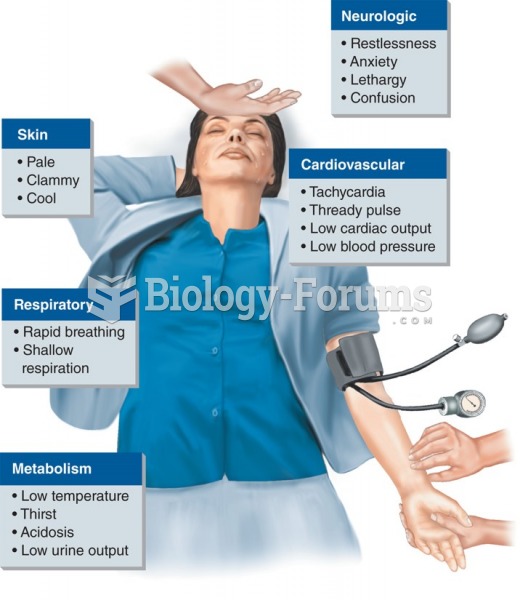
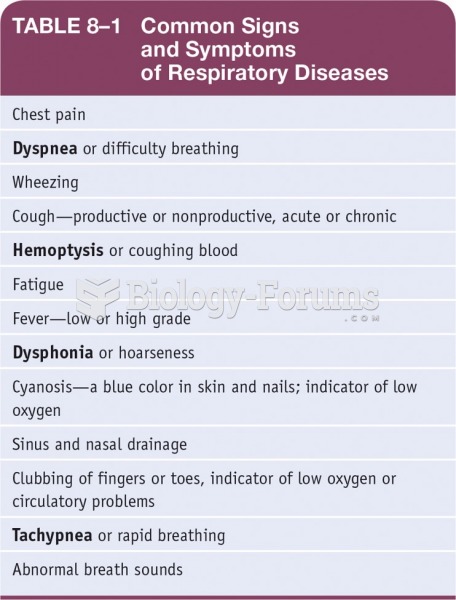
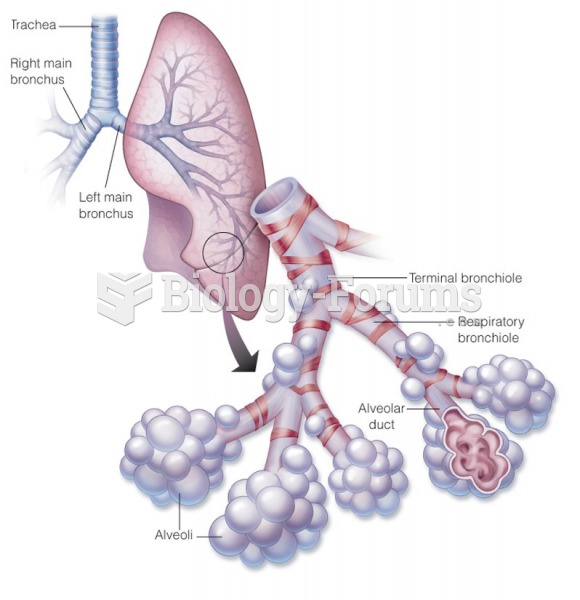
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Did you know?
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
Did you know?
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
Did you know?
All adults should have their cholesterol levels checked once every 5 years. During 2009–2010, 69.4% of Americans age 20 and older reported having their cholesterol checked within the last five years.
Did you know?
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.