|
|
|
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
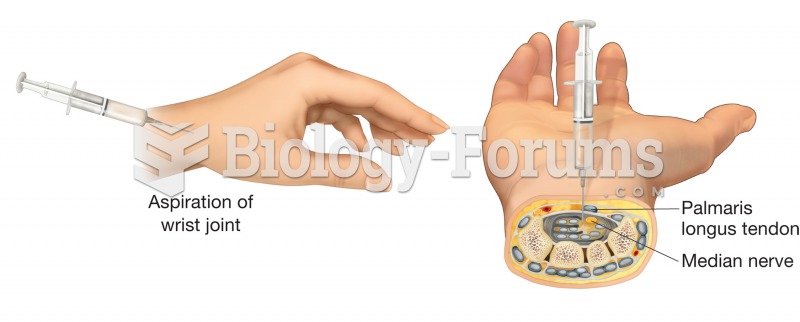
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.