This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
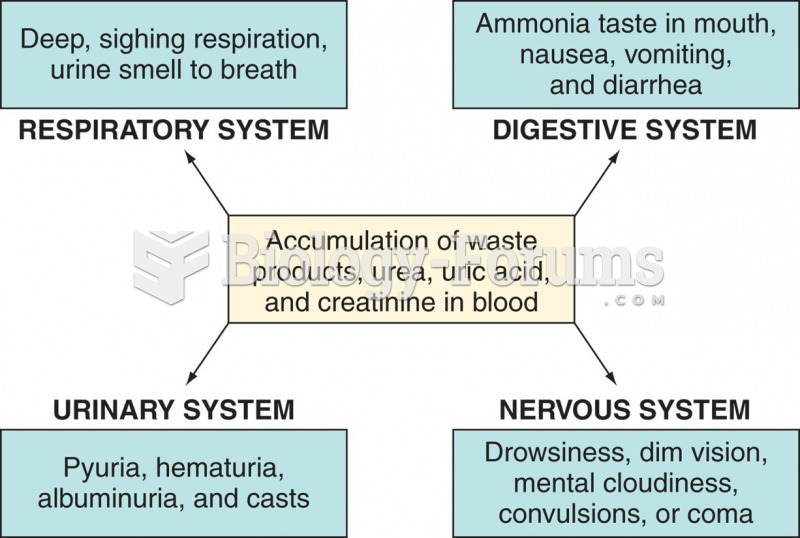
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Did you know?
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Did you know?
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Did you know?
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.