This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Atropine was named after the Greek goddess Atropos, the oldest and ugliest of the three sisters known as the Fates, who controlled the destiny of men.
Did you know?
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
Did you know?
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
Did you know?
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Did you know?
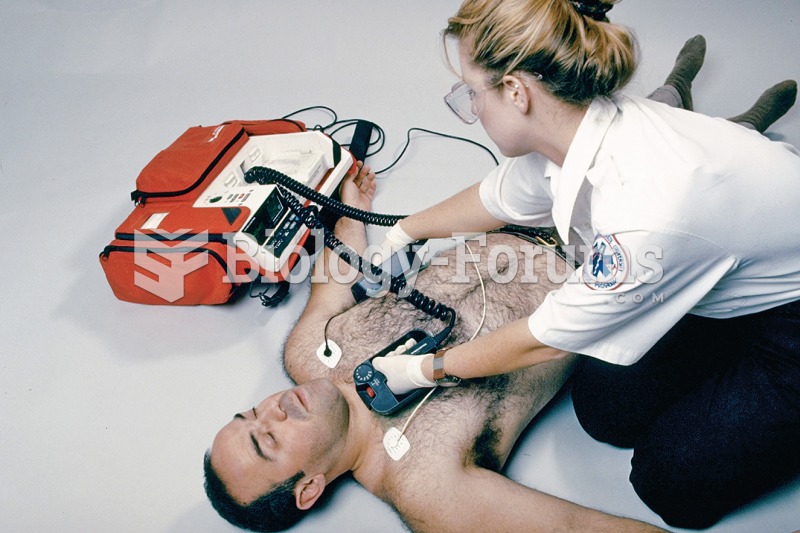
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.