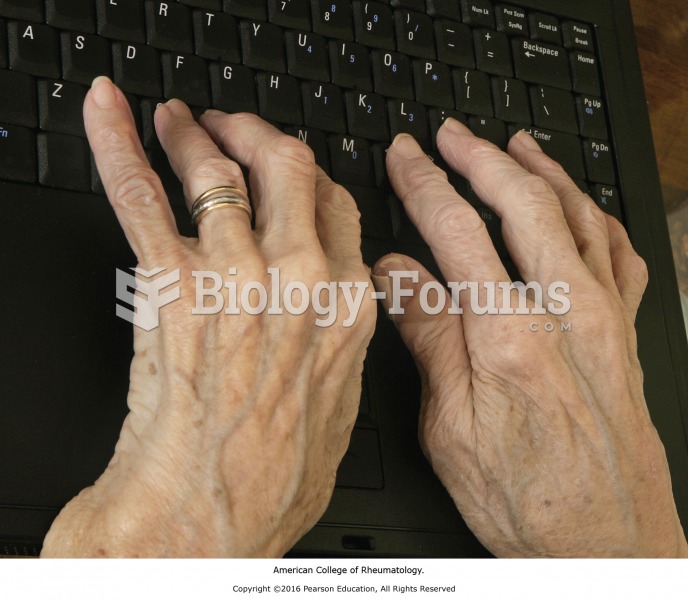
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
Did you know?
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
Did you know?
More than nineteen million Americans carry the factor V gene that causes blood clots, pulmonary embolism, and heart disease.
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Did you know?
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.