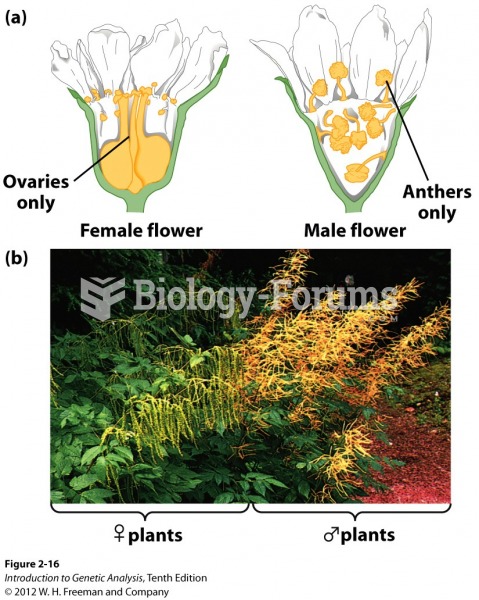
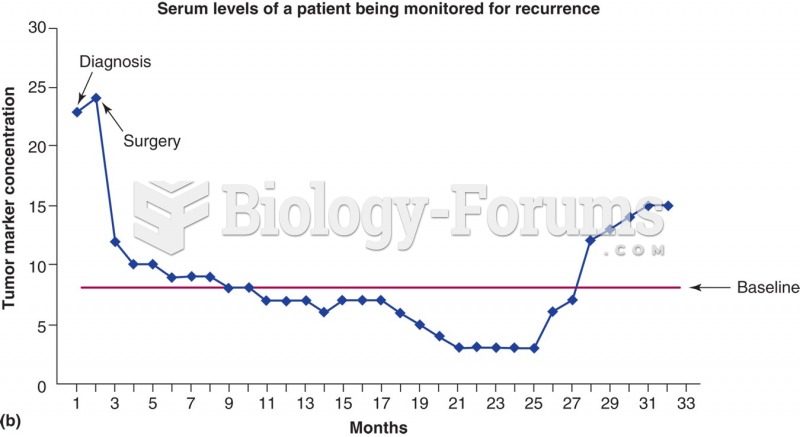
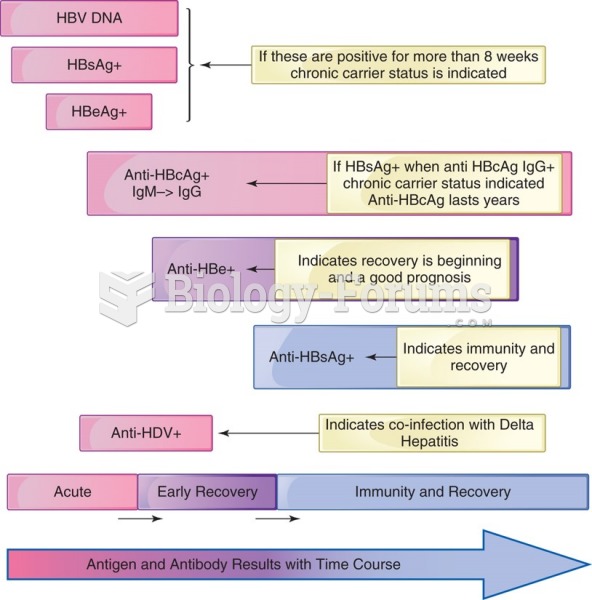
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
Did you know?
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
Did you know?
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Did you know?
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Did you know?
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.