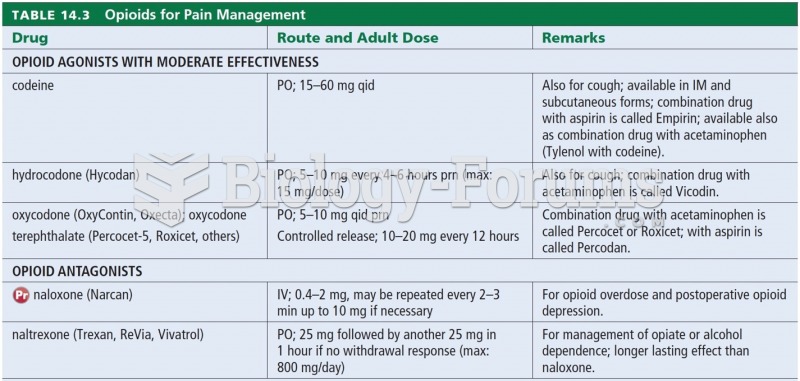
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Lower drug doses for elderly patients should be used first, with titrations of the dose as tolerated to prevent unwanted drug-related pharmacodynamic effects.
Did you know?
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
Did you know?
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
Did you know?
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Did you know?
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.