|
|
|
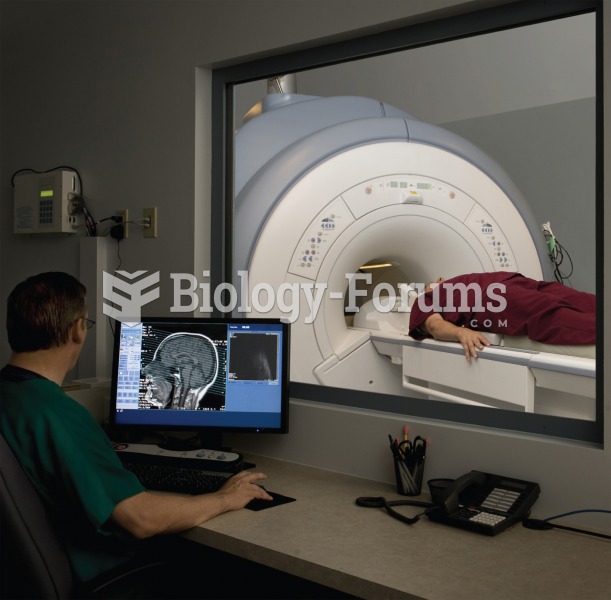
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.