|
|
|
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Only 12 hours after an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, the egg cell starts to divide. As it continues to divide, it moves along the fallopian tube toward the uterus at about 1 inch per day.
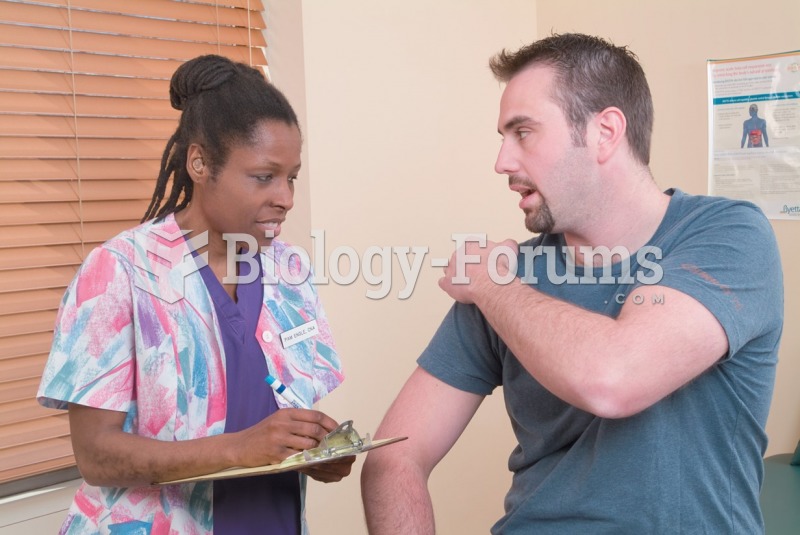
Though newer “smart” infusion pumps are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, they cannot prevent all programming and administration errors. Health care professionals that use smart infusion pumps must still practice the rights of medication administration and have other professionals double-check all high-risk infusions.