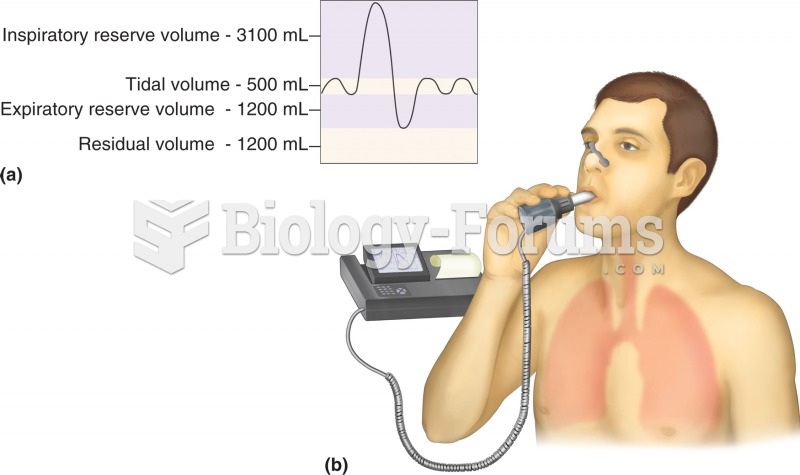
|
|
|
The strongest synthetic topical retinoid drug available, tazarotene, is used to treat sun-damaged skin, acne, and psoriasis.
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.