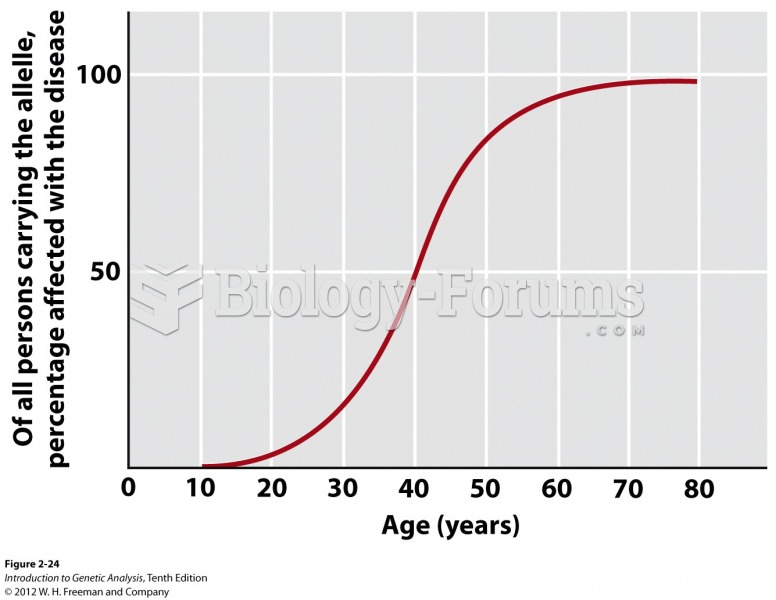
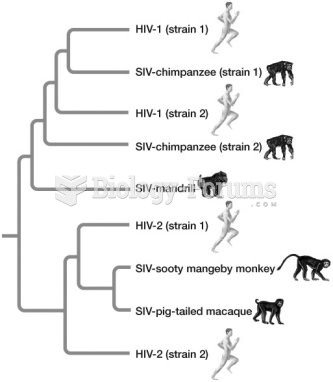
|
|
|
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Asthma cases in Americans are about 75% higher today than they were in 1980.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
 When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
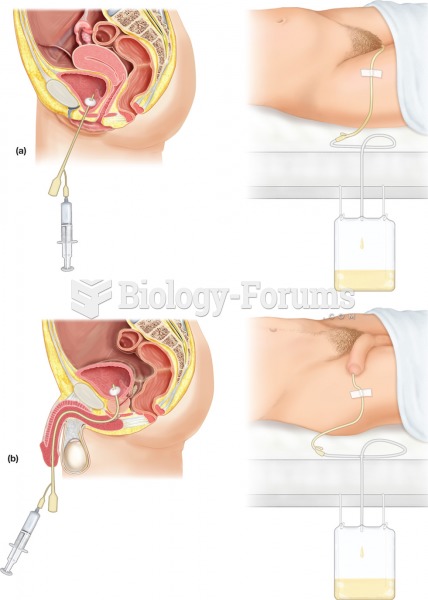 Urinary catheterization. The procedure involves the insertion of a flexible tube, or catheter, throu
Urinary catheterization. The procedure involves the insertion of a flexible tube, or catheter, throu