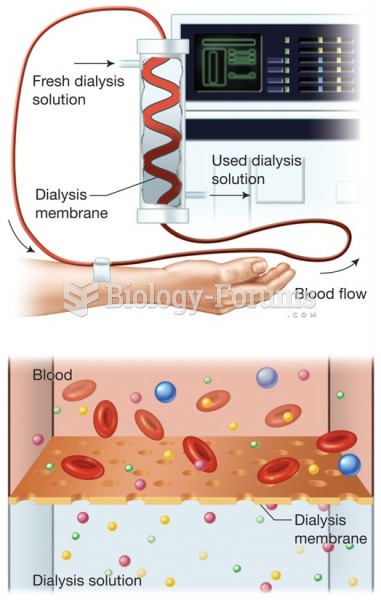
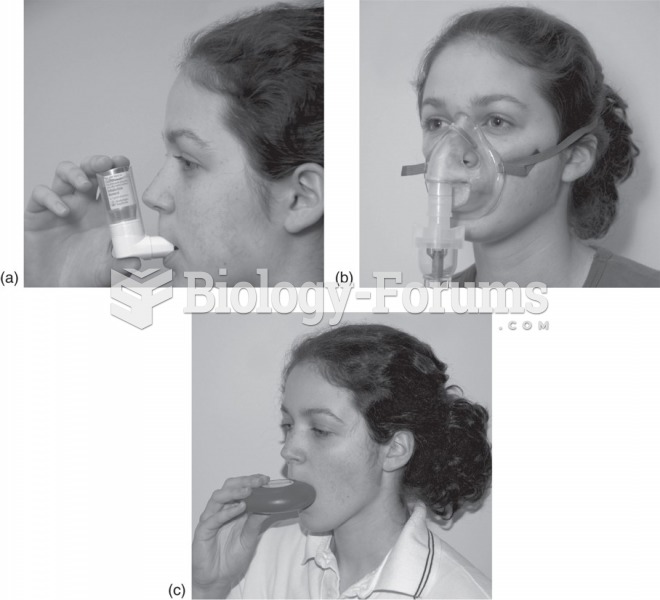
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Did you know?
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
Did you know?
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.