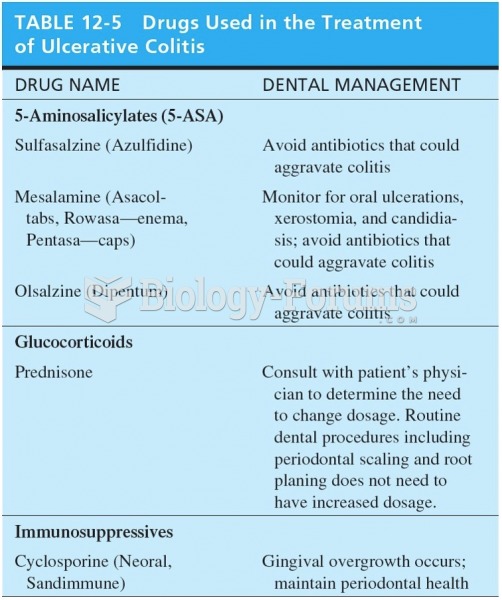
|
|
|
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.