|
|
|
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
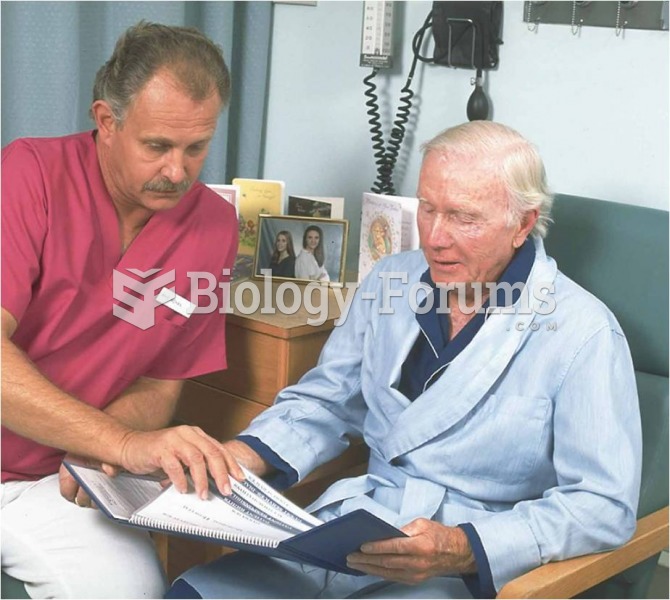
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
About 80% of major fungal systemic infections are due to Candida albicans. Another form, Candida peritonitis, occurs most often in postoperative patients. A rare disease, Candida meningitis, may follow leukemia, kidney transplant, other immunosuppressed factors, or when suffering from Candida septicemia.
Anesthesia awareness is a potentially disturbing adverse effect wherein patients who have been paralyzed with muscle relaxants may awaken. They may be aware of their surroundings but unable to communicate or move. Neurologic monitoring equipment that helps to more closely check the patient's anesthesia stages is now available to avoid the occurrence of anesthesia awareness.