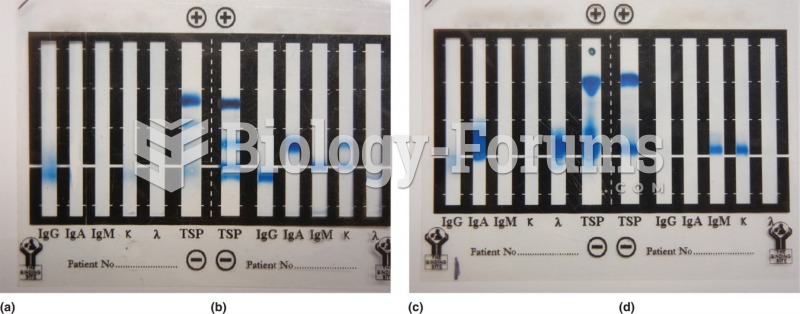
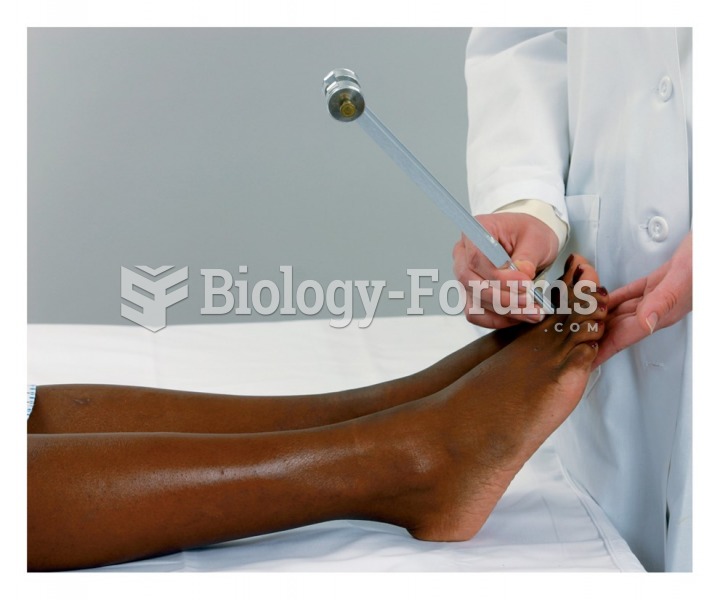
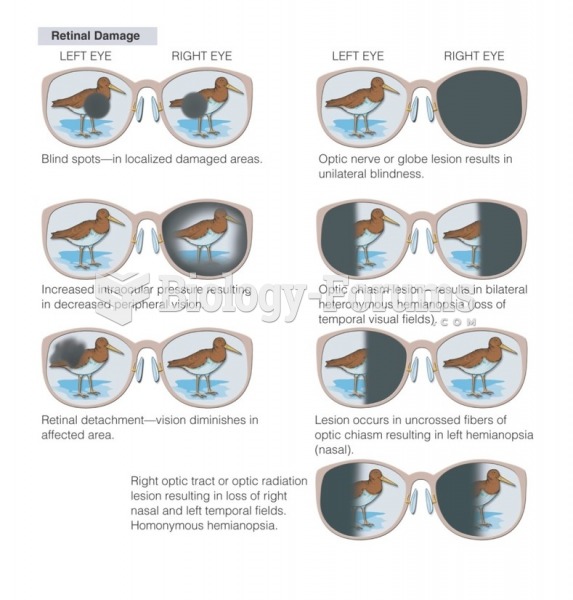
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Aspirin may benefit 11 different cancers, including those of the colon, pancreas, lungs, prostate, breasts, and leukemia.
Did you know?
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
Did you know?
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Did you know?
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Did you know?
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.