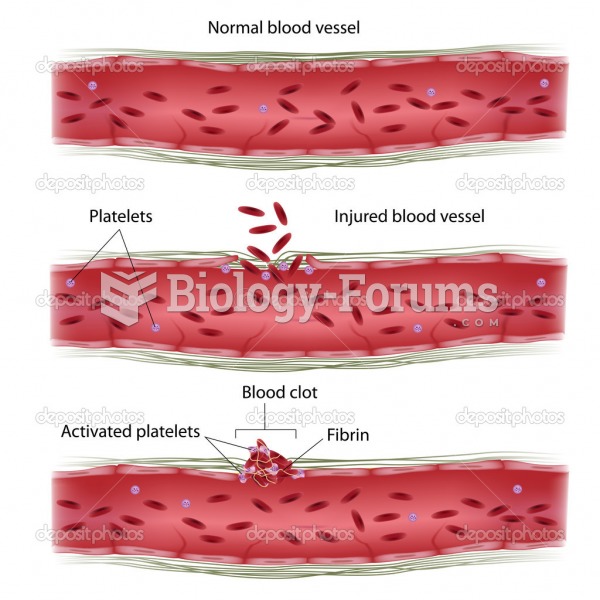
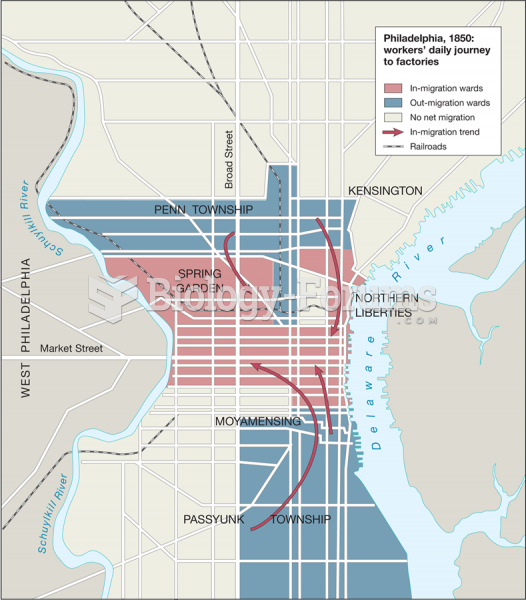
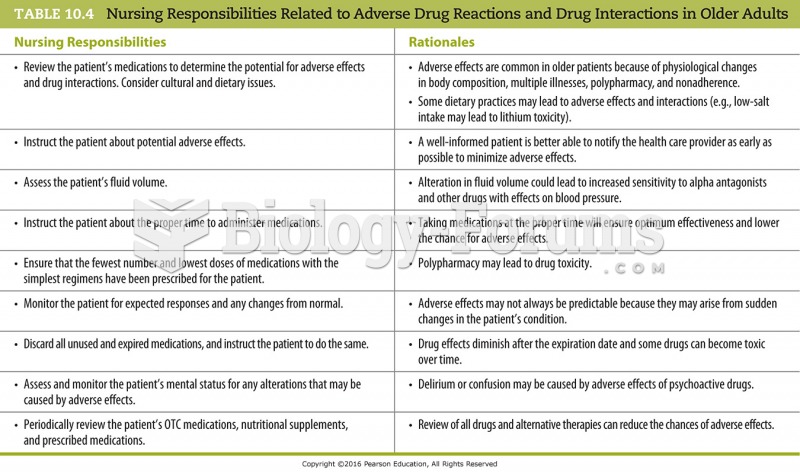
|
|
|
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.
In the ancient and medieval periods, dysentery killed about ? of all babies before they reach 12 months of age. The disease was transferred through contaminated drinking water, because there was no way to adequately dispose of sewage, which contaminated the water.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.