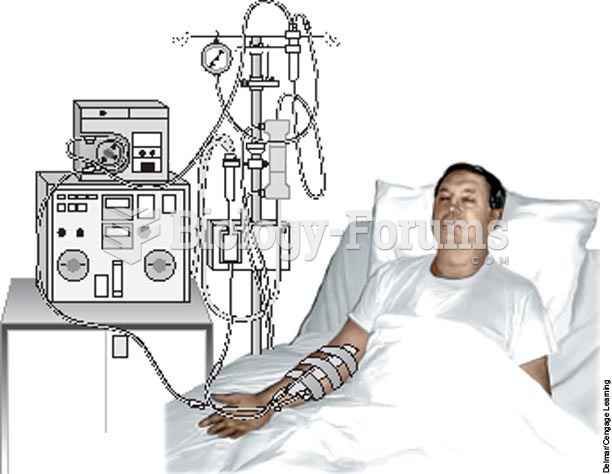
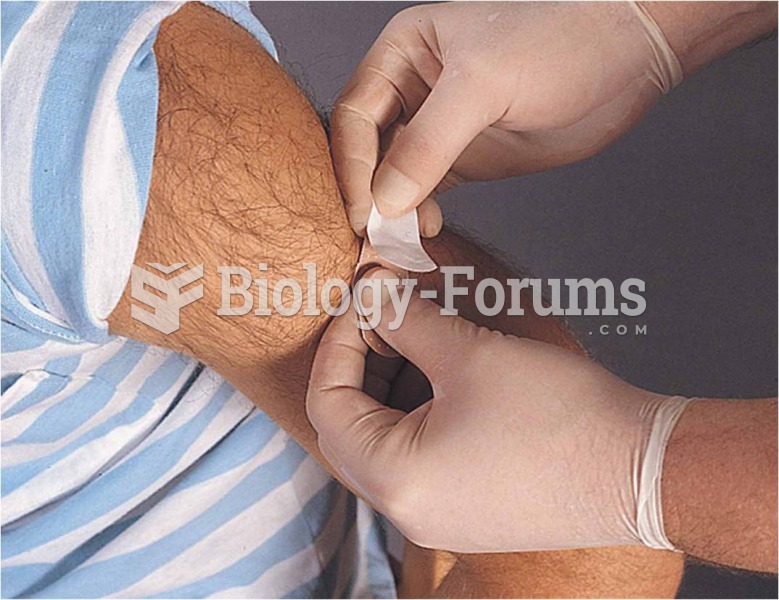
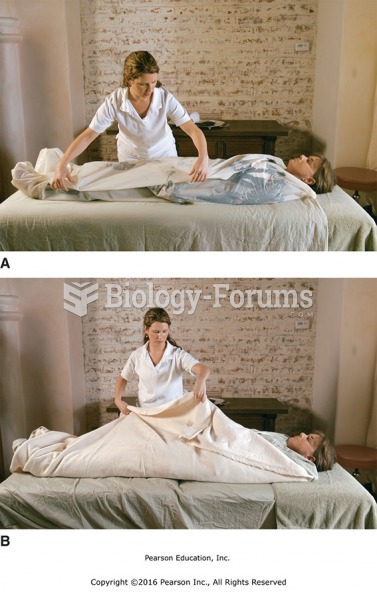
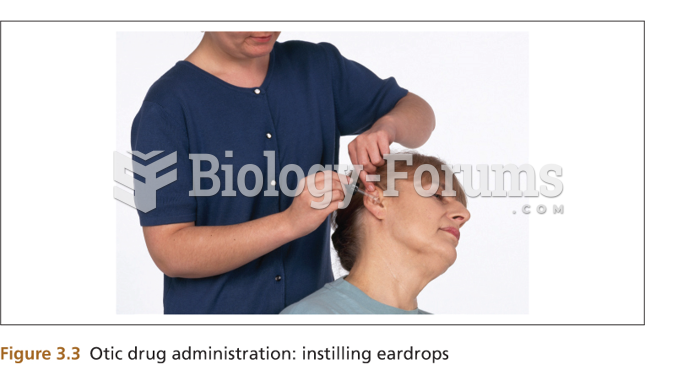
|
|
|
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.