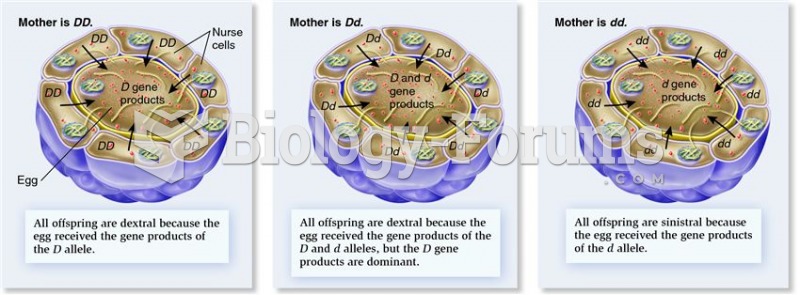
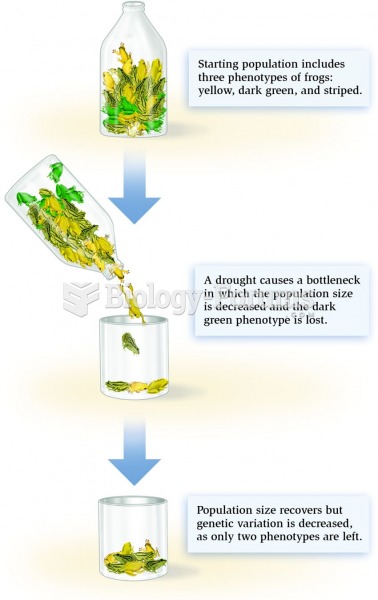
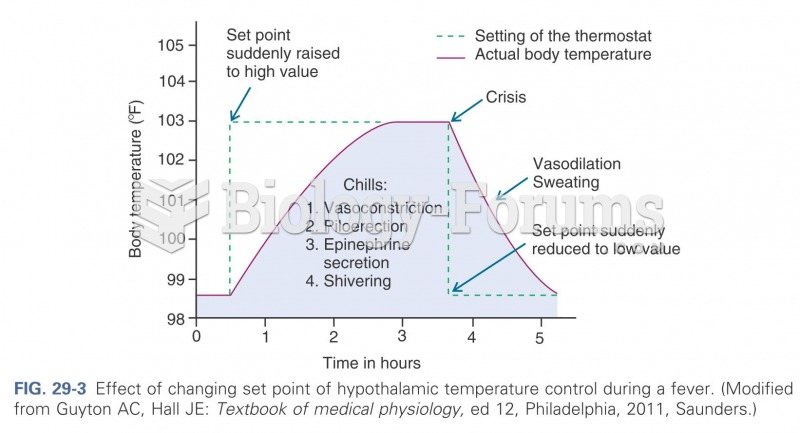
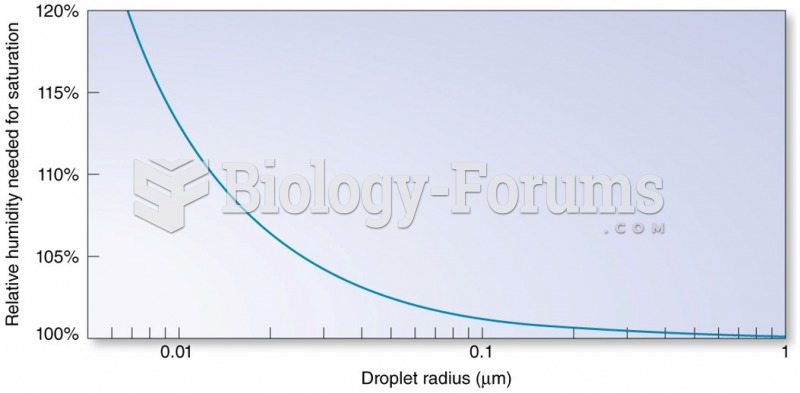
|
|
|
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
It is believed that the Incas used anesthesia. Evidence supports the theory that shamans chewed cocoa leaves and drilled holes into the heads of patients (letting evil spirits escape), spitting into the wounds they made. The mixture of cocaine, saliva, and resin numbed the site enough to allow hours of drilling.