This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Did you know?
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Did you know?
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
Did you know?
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
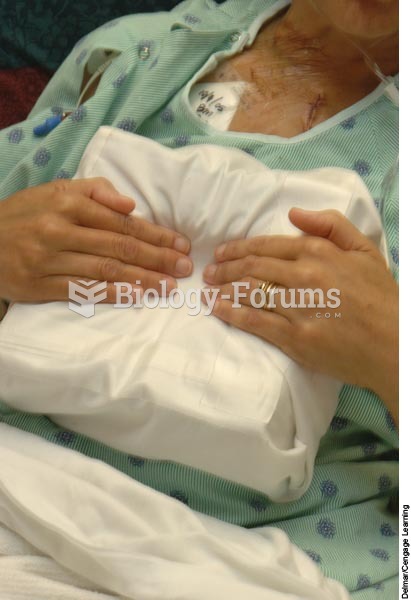 The postoperative client supports an incision with a folded pillow when taking a deep breath and cou
The postoperative client supports an incision with a folded pillow when taking a deep breath and cou
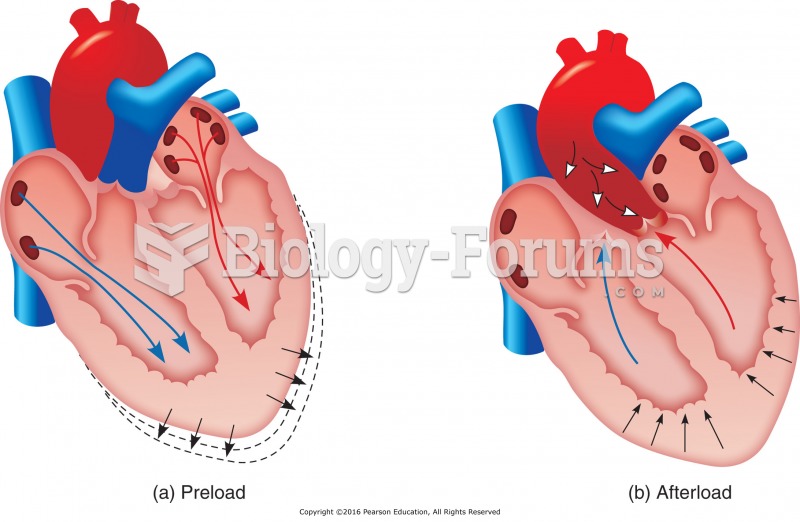 a) Preload is the degree to which the ventricles are filled with blood and the myocardial fibers are ...
a) Preload is the degree to which the ventricles are filled with blood and the myocardial fibers are ...