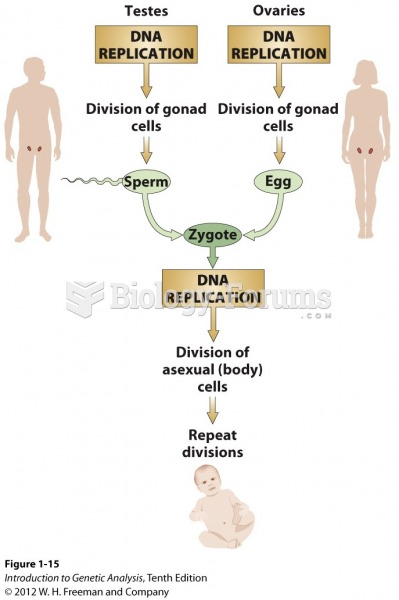
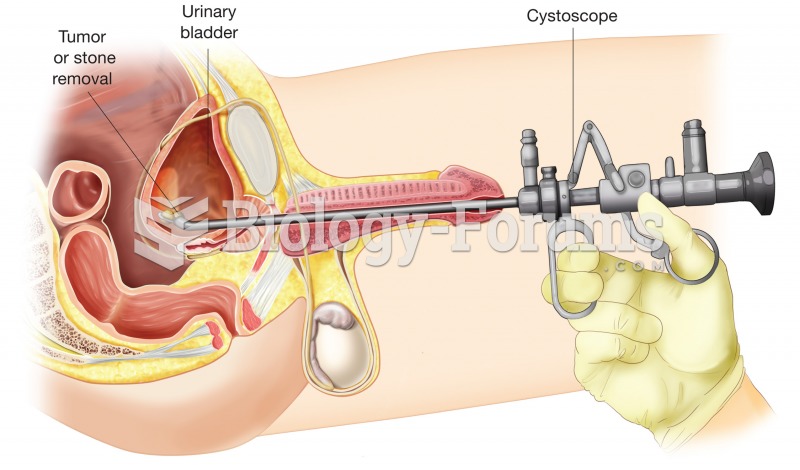
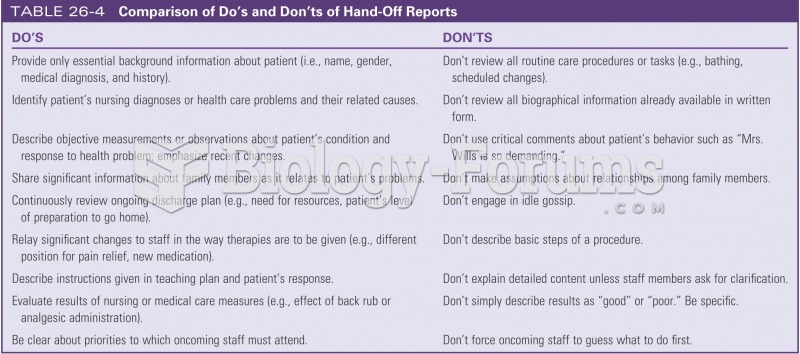
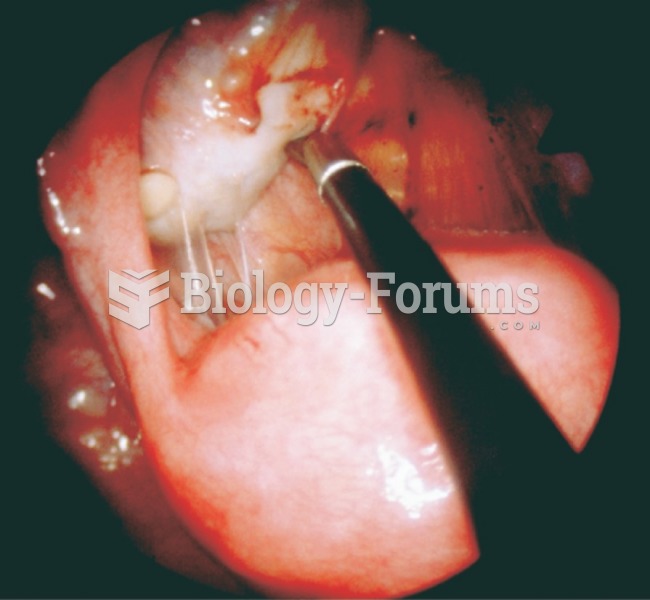
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Did you know?
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Did you know?
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Did you know?
Between 1999 and 2012, American adults with high total cholesterol decreased from 18.3% to 12.9%
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.