|
|
|
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
Long-term mental and physical effects from substance abuse include: paranoia, psychosis, immune deficiencies, and organ damage.
The average older adult in the United States takes five prescription drugs per day. Half of these drugs contain a sedative. Alcohol should therefore be avoided by most senior citizens because of the dangerous interactions between alcohol and sedatives.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
 When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
When using an interpreter, the nurse should pose questions directly to the patient, not the interpre
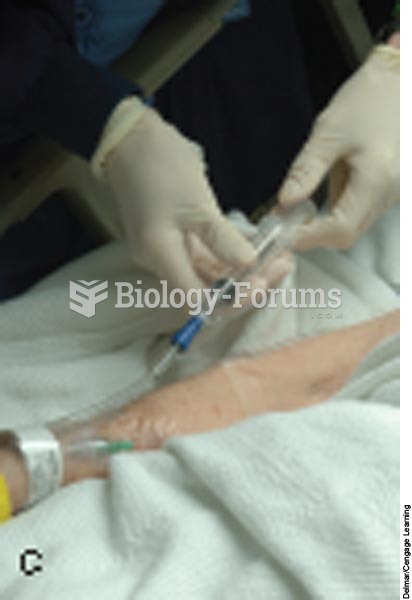 Injecting an IV push (bolus) medication; C, another type of needleless syringe and needleless IV acc
Injecting an IV push (bolus) medication; C, another type of needleless syringe and needleless IV acc