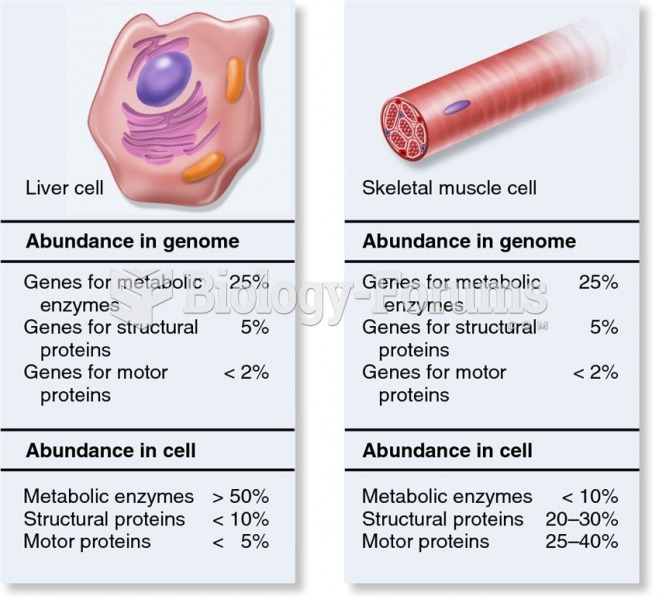
|
|
|
Medication errors are more common among seriously ill patients than with those with minor conditions.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
Cyanide works by making the human body unable to use oxygen.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
 Children with Down syndrome have a small head, short, thick neck, flattened face, and a distinctive ...
Children with Down syndrome have a small head, short, thick neck, flattened face, and a distinctive ...
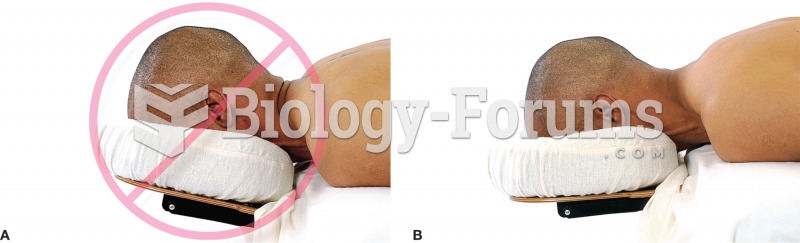 a) Avoid placing the face cradle too high because it hyperextends and strains the neck. b) When the ...
a) Avoid placing the face cradle too high because it hyperextends and strains the neck. b) When the ...