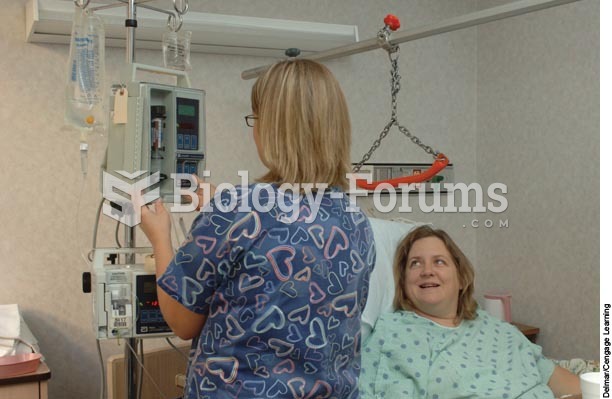|
|
|
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.