Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Assessing the neuromuscular status of the client will not differentiate between the two conditions.
Rationale 2: Asking the client about family and occupational history is helpful, but not diagnostic.
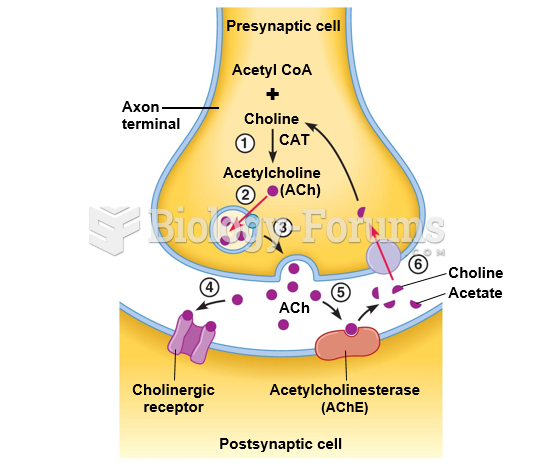
Rationale 3: Assessing serum levels of the cholinesterase inhibitor does not correlate with physical symptoms.
Rationale 4: This is a diagnostic test for myasthenic crisis.
Global Rationale: Administering edrophonium and monitoring the client's response is a diagnostic test for myasthenic crisis. Assessing the neuromuscular status of the client will not differentiate between the two conditions. Asking the client about family and occupational history is helpful, but not diagnostic. Assessing serum levels of the cholinesterase inhibitor does not correlate with physical symptoms.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Weakness that occurs 3 or more hours after drug administration without muscarinic overstimulation is more likely due to myasthenic crisis caused by underdosing and is treated with more intensive therapy.
Rationale 2: Weakness that occurs 3 or more hours after drug administration without muscarinic overstimulation is more likely due to myasthenic crisis caused by drug resistance and is treated with more intensive therapy.
Rationale 3: A lower dose of the medication would cause more acute symptoms of weakness.
Rationale 4: Myasthenia gravis is a disease affecting skeletal muscle. It is not a disorder of the autonomic nervous system.
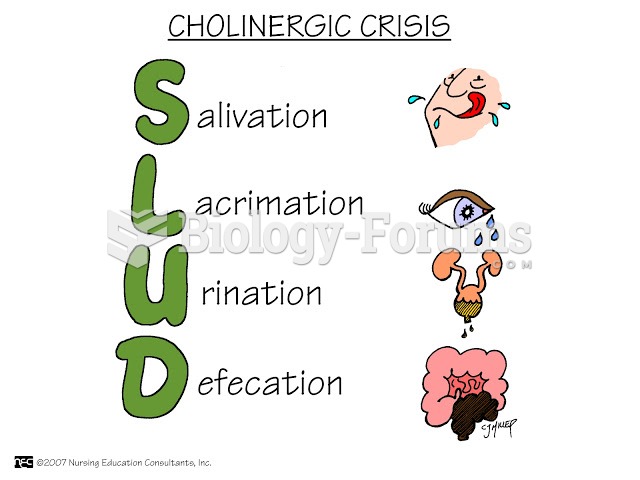
Rationale 5: Atropine is used in the event of muscarinic overstimulation or overdose.
Global Rationale: Weakness that occurs 3 or more hours after drug administration without muscarinic overstimulation is more likely due to myasthenic crisis caused by underdosing or drug resistance and both are treated with more intensive therapy. A lower dose of the medication would cause more acute symptoms of weakness. Myasthenia gravis is a disease affecting skeletal muscle. It is not a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. Atropine is used in the event of muscarinic overstimulation or overdose.