|
|
|
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
Only 12 hours after an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, the egg cell starts to divide. As it continues to divide, it moves along the fallopian tube toward the uterus at about 1 inch per day.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
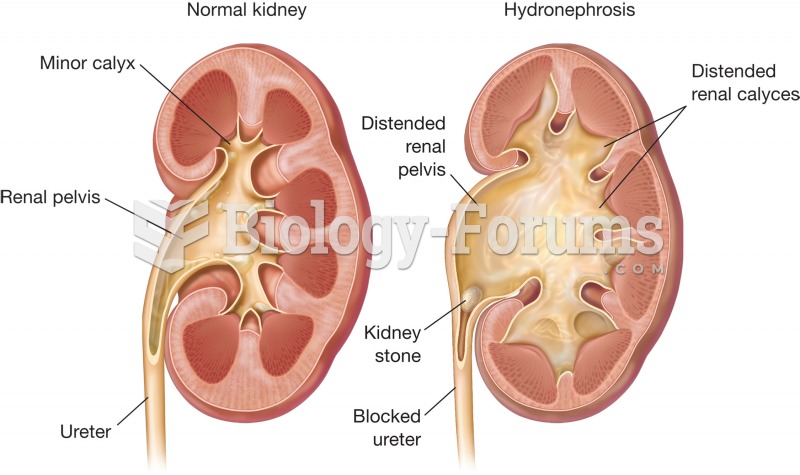
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.