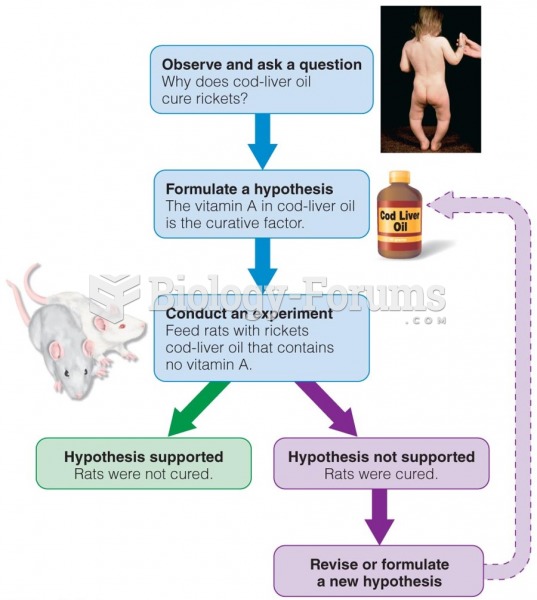
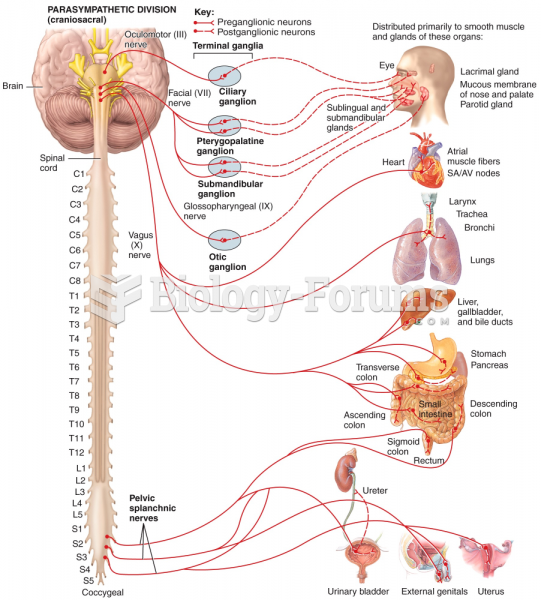
|
|
|
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.