Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1
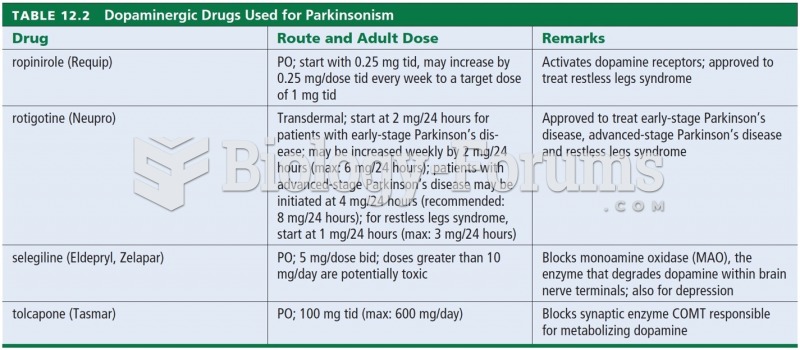
Rationale 1: Anticholinergic drugs inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system, producing similar responses to those produced by sympathomimetics.
Rationale 2: Muscarinic agonists are opposite actions of the sympathetic nervous system.
Rationale 3: Parasympathomimetic s are opposite actions of the sympathetic nervous system.
Rationale 4: Adrenergic antagonists are opposite actions of the sympathetic nervous system.
Global Rationale: Anticholinergic drugs inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system, producing similar responses to those produced by sympathomimetics. Muscarinic agonists, parasympathomimetic s, and adrenergic antagonists all produce opposite actions of the sympathetic nervous system.
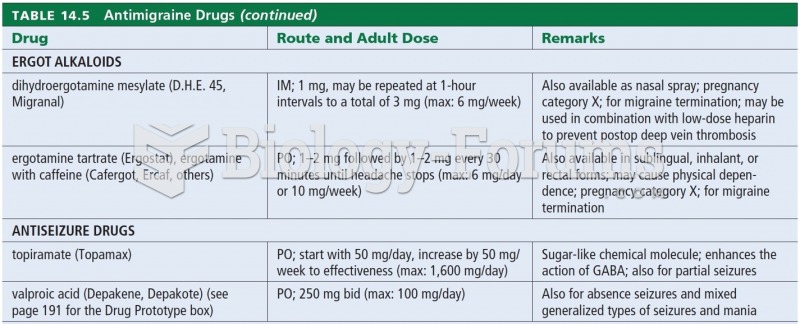
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as heart rate.
Rationale 2: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as blood pressure.
Rationale 3: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as pupil size.
Rationale 4: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as intestinal motility.
Rationale 5: Although the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions, fluid volume is not under the control of the nervous system.
Global Rationale: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, pupil size, and intestinal motility. Although the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions, fluid volume is not under the control of the nervous system.