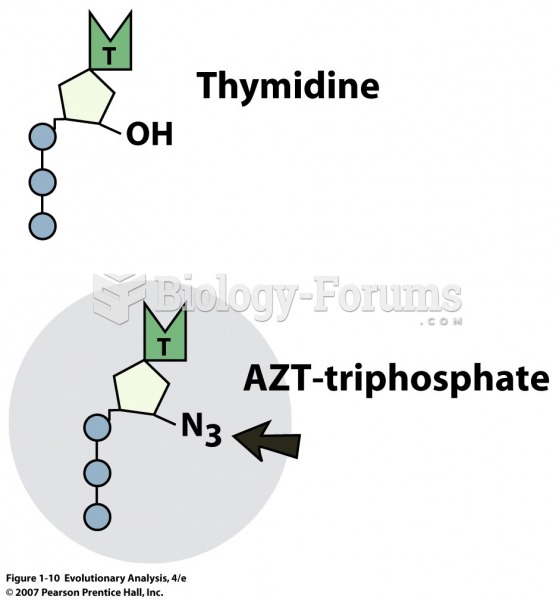
|
|
|
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).