This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
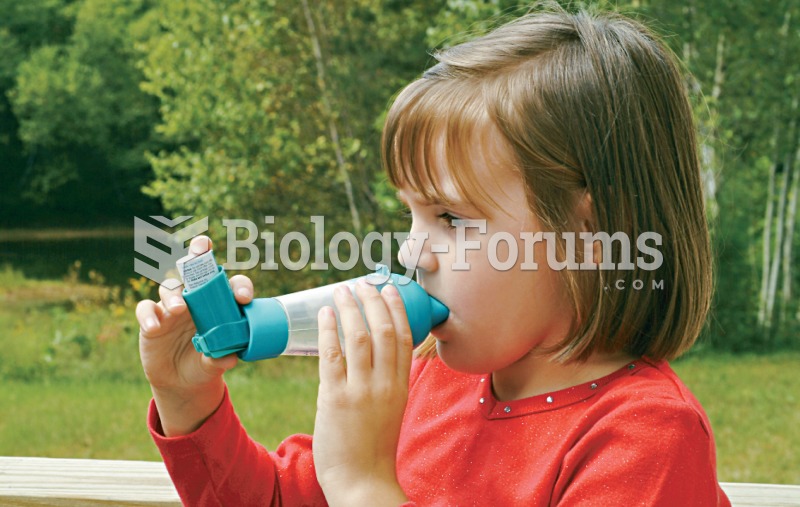
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
If you could remove all of your skin, it would weigh up to 5 pounds.
Did you know?
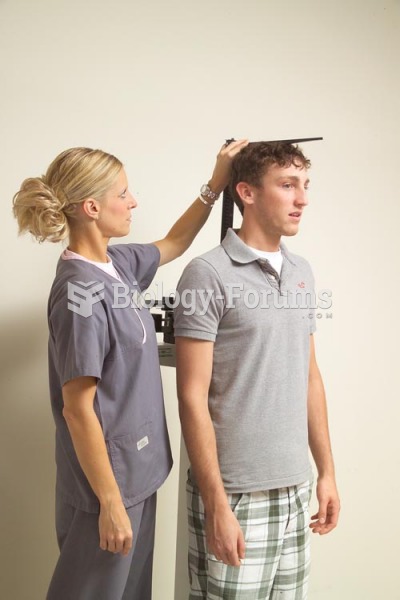
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.