|
|
|
The first-known contraceptive was crocodile dung, used in Egypt in 2000 BC. Condoms were also reportedly used, made of animal bladders or intestines.
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
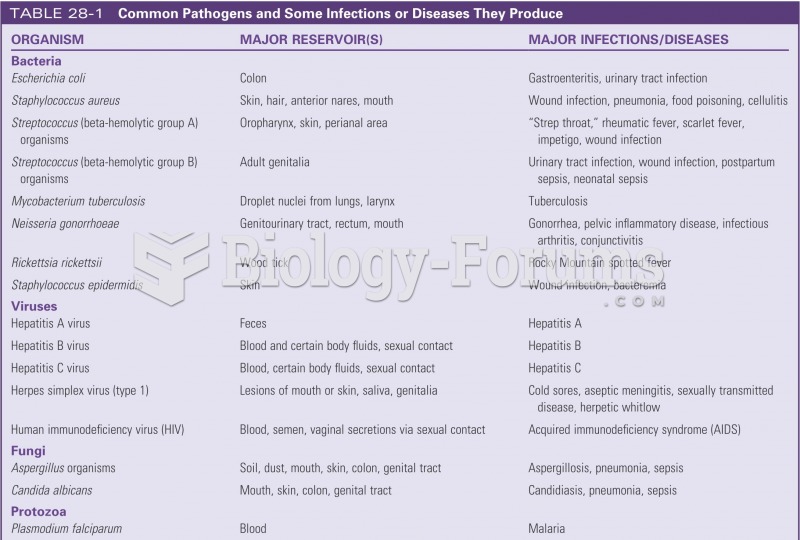
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.