|
|
|
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.
In 1864, the first barbiturate (barbituric acid) was synthesized.
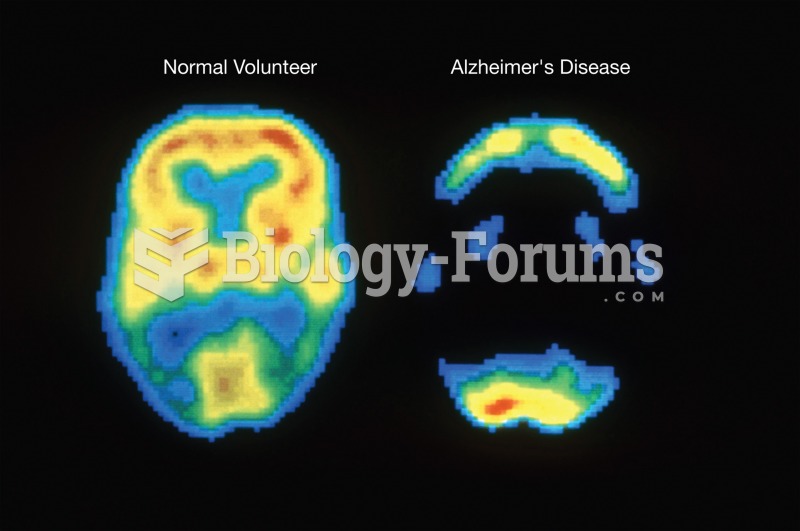
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.