|
|
|
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
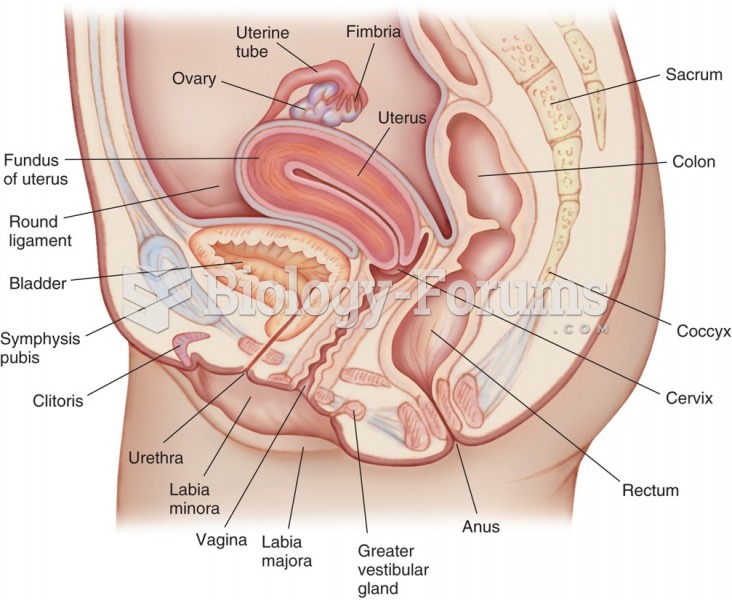
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.