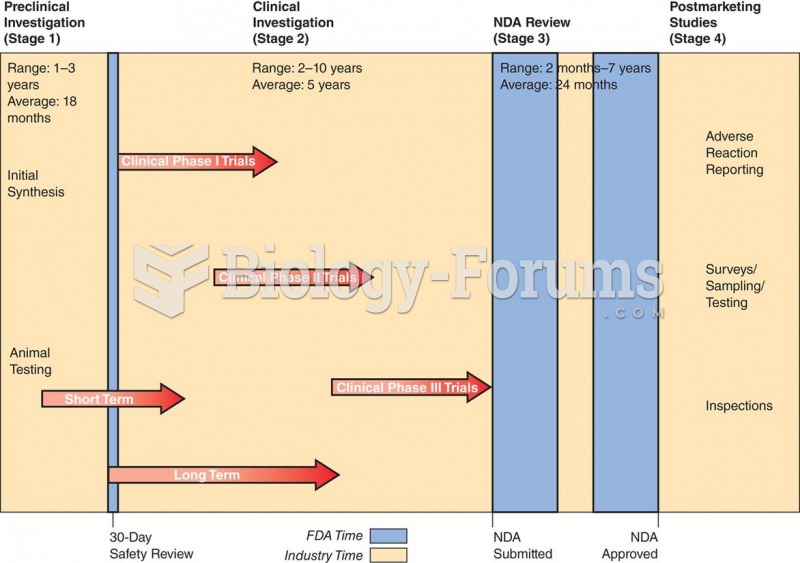
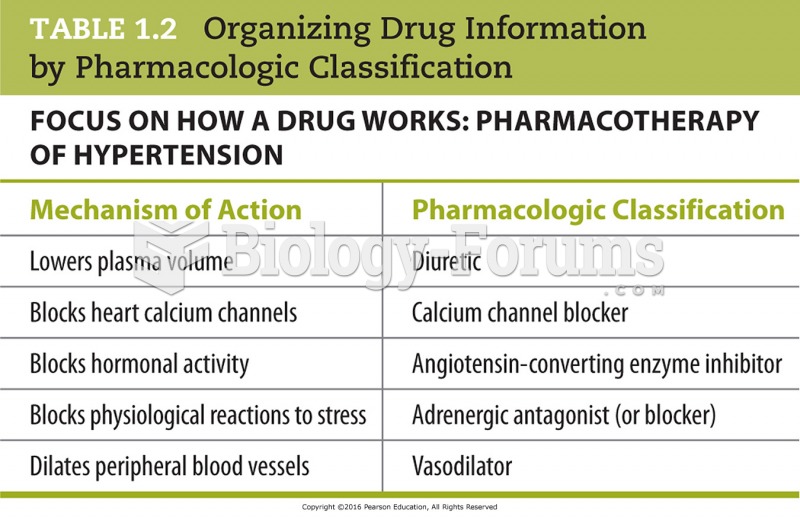
|
|
|
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Colchicine is a highly poisonous alkaloid originally extracted from a type of saffron plant that is used mainly to treat gout.
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
 The tone of the nurse-patient introduction sets the stage for the patient interview and patient care
The tone of the nurse-patient introduction sets the stage for the patient interview and patient care
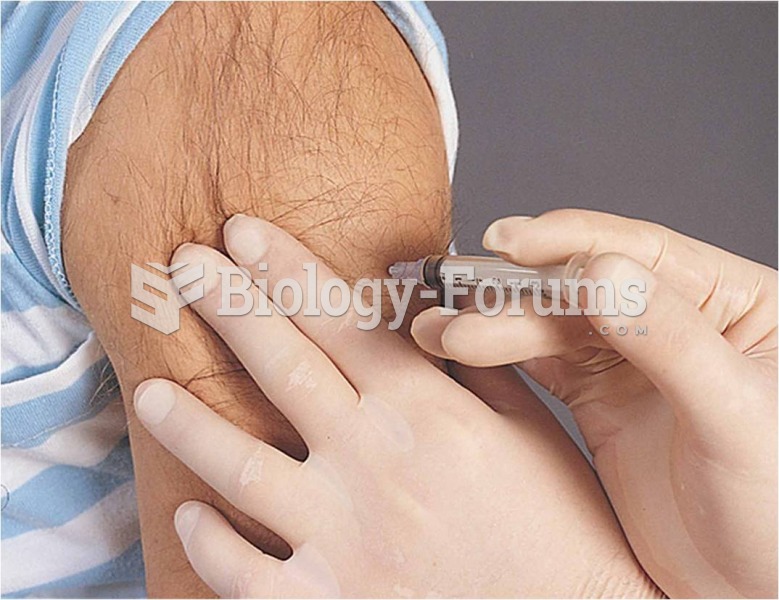 Intramuscular drug administration: (c) the needle is inserted at a 90° angle: Source: Pearson Educat
Intramuscular drug administration: (c) the needle is inserted at a 90° angle: Source: Pearson Educat